Marrow transplantation is the process of transplanting stem cells, which are responsible for making healthy blood, into the patient’s body in order to treat some diseases in the person.
- How Is a Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant Done?
- Why Is a Bone Marrow Transplant Needed?
- What Are Some Diseases That May Benefit from Bone Marrow Transplants?
- Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
- What Are the Risks of Bone Marrow Transplantation?
- What Is Done Before Bone Marrow Transplantation?
- What To Consider Before a Transplant?
- Bone Marrow Transplant Prices in Turkey
- How Long Does a Marrow Transplantation Patient Live?
- How Many Days Does a Marrow Donor Heal?
- What is the Survival Rate for Bone Marrow Transplants?
- Is a Bone Marrow Transplant a Major Surgery?
- Is Bone Marrow Transplant 100% Successful?
- Can You Live a Healthy Life After a Bone Marrow Transplant?
This marrow transplant is needed when the body does not produce healthy blood due to leukemia, lymphoma, blood cancers, or hereditary disorders. There are two treatment methods to be applied to patients who need bone marrow for a number of reasons. In the method called autologous; Cells taken from the patient’s own body are transferred to the patient again. Another treatment method is allogeneic transplantation; where Cells taken from another person are transplanted into the patient.
Bone marrow transplantation is done by opening a vascular access to the patient and care should be taken during this procedure. It is important that this procedure, which is a heavy surgical intervention, is performed under the control of a doctor with sterilized spaces and instruments.
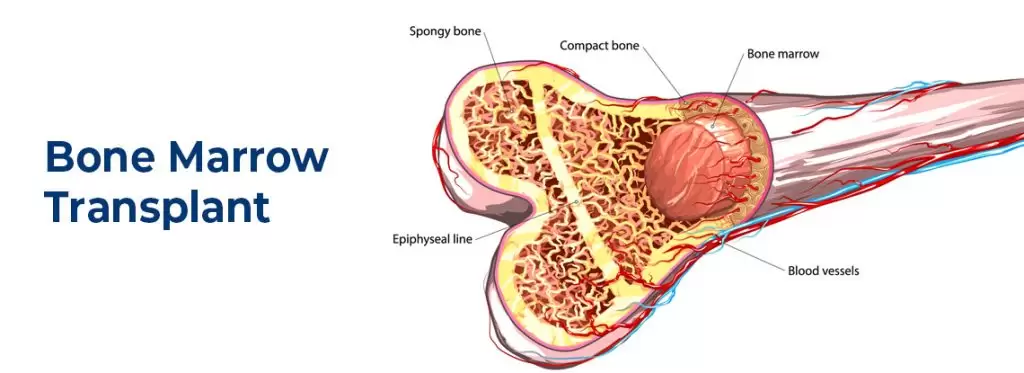
How Is a Bone Marrow (Stem Cell) Transplant Done?
As in the treatment of every disease, the patient should first be examined in detail in diseases such as marrow transplantation This examination is done using a number of tests and examinations and may take several days.
Before the marrow transplant, a tube called a catheter is inserted into one of the large veins in the patient’s chest or neck region. Thanks to this tube, which is not removed during the treatment process, transplantation is performed.
Doctors decide where to get the stem cells to be given to the person. These cells are either taken from the patient himself or from another donor.
The process of taking stem cells from the patient’s own body takes place as follows:
- The stem cells in the body need to be increased and mixed with the blood in order for these cells to be taken easily. For this, an injection process called growth factor is applied daily.
- Then the apheresis process is started. Blood is taken from the person’s vein and this blood is circulated in a machine. This special device separates the blood into its cells. The necessary stem cells taken from it are frozen and wait for the transplant order.
- The remaining blood is returned to the patient’s body.
Another method is to take bone marrow from a donor. For this, a donor whose blood and tissues are suitable is found and after the necessary tests and examinations, it is decided whether the stem cells will be taken from the blood or marrow and the process is started.
Another method is transplanting stem cells from the umbilical cord. In some cases, parents choose to freeze the blood in the umbilical cord as soon as their baby is born, just in case. In any case, this blood is used. Or, for the sick child, the parents use the blood from the umbilical cord of the child who was born with another child.
Why Is a Bone Marrow Transplant Needed?
A bone marrow transplant may be needed to treat a variety of conditions, including:
Cancer: Bone marrow transplants are often used to treat blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Inherited disorders: Bone marrow transplants can also be used to treat inherited disorders, such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
Autoimmune disorders: Bone marrow transplants may be used to treat autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Infections: Bone marrow transplants may be used to treat infections that are not responding to other treatments.
The decision to have a bone marrow transplant is a serious one, and it is important to discuss all of the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Here are some other factors that may be considered when deciding whether or not to have a bone marrow transplant:
The patient’s age and overall health: Younger patients are generally better candidates for bone marrow transplants.
The type of cancer or condition: Some cancers and conditions are more responsive to bone marrow transplants than others.
The availability of a suitable donor: A bone marrow transplant can be successful only if the patient receives healthy bone marrow cells from a compatible donor.
What Are Some Diseases That May Benefit from Bone Marrow Transplants?
A bone marrow transplant is a medical procedure that replaces diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found in the center of bones. It is responsible for producing blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
A bone marrow transplant may be used to treat a variety of diseases, including:
Cancer: Bone marrow transplants are often used to treat blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
Inherited disorders: Bone marrow transplants can also be used to treat inherited disorders, such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
Autoimmune disorders: Bone marrow transplants may be used to treat autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Infections: Bone marrow transplants may be used to treat infections that are not responding to other treatments.
The decision to have a bone marrow transplant is a serious one, and it is important to discuss all of the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Here are some of the diseases that may benefit from a bone marrow transplant:
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): AML is a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow. It is the most common type of leukemia in adults. A bone marrow transplant may be used to treat AML that has not responded to other treatments, or that has come back after treatment.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): ALL is a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow. It is the most common type of leukemia in children. A bone marrow transplant may be used to treat ALL that has not responded to other treatments, or that has come back after treatment.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): CML is a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow. It is a slow-growing cancer, and it is often treated with medication. However, a bone marrow transplant may be used to treat CML that has not responded to other treatments, or that has come back after treatment.
Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a type of cancer that starts in the lymphatic system. There are many different types of lymphoma, and a bone marrow transplant may be used to treat some types of lymphoma that have not responded to other treatments.
Sickle cell disease: Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder that affects the red blood cells. It can cause a variety of problems, including anemia, pain, and organ damage. A bone marrow transplant may be used to treat sickle cell disease in some cases.
Thalassemia: Thalassemia is an inherited disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Thalassemia can cause a variety of problems, including anemia, fatigue, and organ damage. A bone marrow transplant may be used to treat thalassemia in some cases.
These are just a few of the diseases that may benefit from a bone marrow transplant. The decision to have a bone marrow transplant is a serious one, and it is important to discuss all of the risks and benefits with your doctor.
Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant
Autologous bone marrow transplantation is a treatment method that is performed by sending stem cells taken from the person’s own body to their own body. Usually, if the patient’s body produces enough stem cells, the autologous treatment method is used. These stem cells, which were previously taken and stored, are needed in cases where the patient is exposed to excessive chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
- Hodgkin lymphoma disease
- myeloma disease
- non-Hodgkin’s disease
- The autologous treatment method is used for conditions such as plasma cell disorders
The biggest advantage of this method is that the person’s body recognizes its own cells. In this way, incompatibility is not observed.
Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
In allogeneic stem cell transplantation, the stem cells to be given to the patient’s body must be obtained from a donor. This donor could be :
- a family member
- a relative
- a friend or a complete stranger.
In this case, there are three ways to obtain stem cells:
- Stem cells collected from the blood of the person who wants to donate
- Stem cells taken from the hip bone of the person who wants to donate
- Stem cells collected from donated cord blood
Before the donation process is made, a high rate of radiation or chemotherapy is applied to the donor in order to destroy the harmful cells in the donor’s body. In this way, while harmful cells are destroyed, healthy cells are prepared for transplantation. It is possible to treat many diseases, including the following diseases, with donated blood:
- Acute Leukemia Disease
- Adrenoleukodystrophy Disease
- The state of excessive anemia
- Bone marrow failure diseases
- chronic leukemia disease
- Hemoglobinopathies Disease
- Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease
- Deficiencies in the person’s immunity
- Errors in inborn metabolism
- Multiple Myeloma Disease
- Myelodysplastic Diseases
- Neuroblastoma Disease
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Disease
What Are the Risks of Bone Marrow Transplantation?
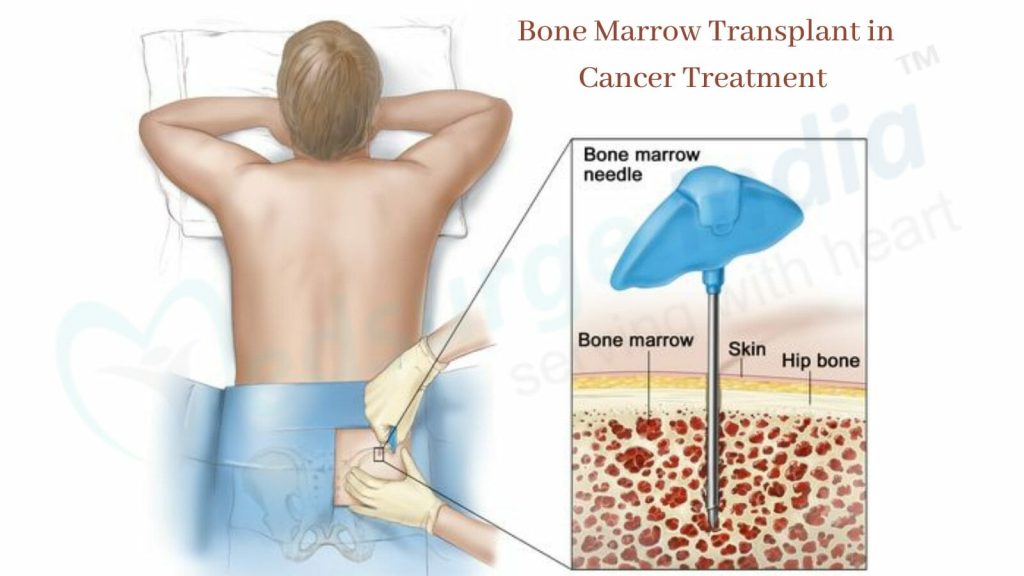
Diseases requiring bone marrow transplantation are usually serious diseases. For this reason, there are some risks in bone marrow transplantation, which is an extremely important surgical procedure. In order to minimize these risks, it is necessary to cooperate with the doctor from the stage of deciding to have a bone marrow transplant and fulfill what he says.
All possible risks should be shared with the patient and their relatives by the doctor. We can list these possible risks and complications as follows:
- High risk of infection
- Anemia risk
- Excessive bleeding risk
- Formation of bruises
- In allogeneic transplant only, the risk of Host disease, Graft disease, Versus disease
- The risk of stem cell failure
- Risk of damage to organs
- The risk of cataracts
- Risk of infertility
- Risk of developing certain cancers
What Is Done Before Bone Marrow Transplantation?
First of all, after the decision for stem cell transplantation, the patient is subjected to a number of tests and examinations to check whether he is ready for transplantation. If he is ready, he places a tube in one of the large veins in the neck or chest, which will also be used during the transplant process.
Then it is decided where to get the stem cells. If the autologous treatment method is decided, stem cells are taken from the person and frozen until the transplantation process. If stem cells are to be obtained with the allogeneic treatment method, stem cells are collected from a donor and kept until transplantation.
What To Consider Before a Transplant?
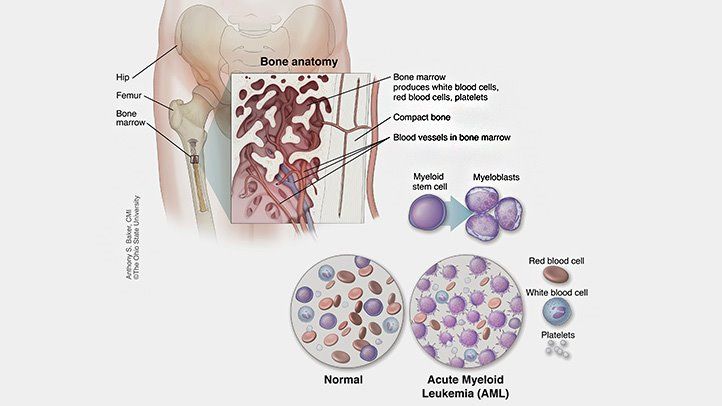
Here are the factors to consider before a transplant:
The type of transplant: There are many different types of transplants, each with its own set of considerations. For example, a kidney transplant is different from a heart transplant.
Your health: Your overall health will be a major factor in determining whether or not you are a good candidate for a transplant. You will need to be in good physical and mental health to undergo a transplant.
Your lifestyle: Your lifestyle will also be a factor in the decision-making process. For example, if you are a smoker, you may not be a good candidate for a lung transplant.
The risks and benefits: It is important to weigh the risks and benefits of a transplant before making a decision. Transplants are major surgeries, and they come with risks, such as infection and rejection. However, they can also improve your quality of life.
Your support system: You will need a strong support system to help you through the transplant process. This includes your family, friends, and healthcare team.
Bone Marrow Transplant Prices in Turkey
Turkey continues to be a beacon of hope to patients with its advanced technology and experienced doctors. The treatment of many diseases that require bone marrow transplantation, that is, stem cell transplantation, is safely performed in Turkey with a high recovery rate.
In addition to these high-tech and experienced doctors, they also encounter many positive aspects such as friendly caregivers and staff, hospitals equipped with high technology, a comfortable treatment process, affordable prices, and the opportunity to vacation among the historical beauties of Turkey.
For this reason, if you also want to prefer Turkey for a bone marrow transplant, you can contact us for detailed information, answer your questions, and price information.
How Long Does a Marrow Transplantation Patient Live?
All diseases are personal. Many factors such as the degree of fighting the disease, the stage of the disease, the treatment methods used, the complications that occur during the operation, and the risks of the disease affect the life expectancy.
For this reason, by contacting us, you can ask us any questions you may have about bone marrow transplantation and get information from our doctors.
How Many Days Does a Marrow Donor Heal?
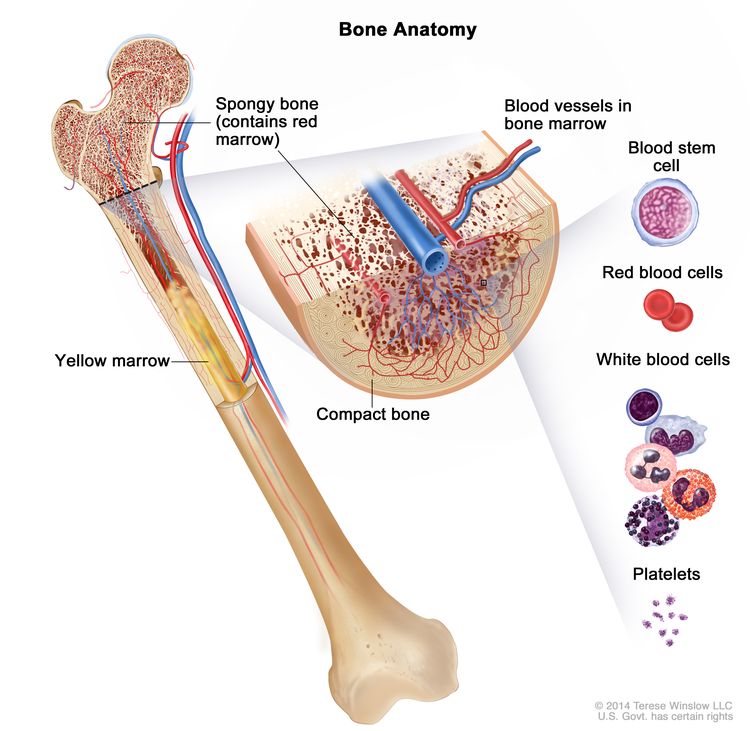
A marrow transplant is usually a treatment method that healthy people are afraid to donate. Although the idea of taking marrow from the hip bone may seem painful to people, this procedure is performed under surgical operation, with the person fully anesthetized or half anesthetized under general or local anesthesia.
For this reason, the donor can donate bone marrow without feeling any pain in a sterile environment. The donor, who regains consciousness after an hour, is kept in the hospital for observation for one day and sent home after the necessary tests are performed the next day.
Although pain is felt in the treated area for about a week, it is possible to return to normal life in a short time.
What is the Survival Rate for Bone Marrow Transplants?
Bone marrow transplants are a life-saving procedure for patients with certain types of blood cancers and disorders. But what is the survival rate for bone marrow transplants? The answer to this question depends on several factors.
Firstly, the type of disease being treated plays a significant role in the survival rate. Patients with acute leukemia, for example, tend to have a lower survival rate compared to those with chronic leukemia. Additionally, the stage of the disease and the overall health of the patient before the transplant are crucial factors.
According to the National Marrow Donor Program, the overall survival rate for bone marrow transplants is around 70%. However, this number can vary widely based on individual circumstances. For example, patients who receive a transplant from a matched sibling donor have a higher chance of survival compared to those who receive an unrelated donor transplant.
It is important to note that survival rates have improved significantly over the years due to advancements in medical technology and a better understanding of the procedure. Today, bone marrow transplants offer hope and a chance at a cure for many patients, but it is essential to consult with medical professionals to understand the specific survival rate for each individual case.
Is a Bone Marrow Transplant a Major Surgery?
A bone marrow transplant, also known as a hematopoietic stem cell transplant, is indeed a major surgery. This complex procedure involves replacing damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It is primarily used to treat various types of cancer, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, as well as certain non-cancerous blood disorders.
During a bone marrow transplant, the patient receives high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy the diseased cells in their bone marrow. Once this is done, the healthy stem cells are infused into the patient’s bloodstream, where they travel to the bone marrow and begin producing new blood cells.
The surgery itself may last several hours, and patients are typically placed under general anesthesia. Recovery from a bone marrow transplant can be a lengthy and challenging process, as it involves managing potential complications such as infections, graft-versus-host disease, and organ damage.
Given the complexity of the procedure and the potential risks involved, a bone marrow transplant is undoubtedly a major surgery. However, it is also a life-saving treatment option for many patients, offering hope for a cure or an improved quality of life.
Is Bone Marrow Transplant 100% Successful?
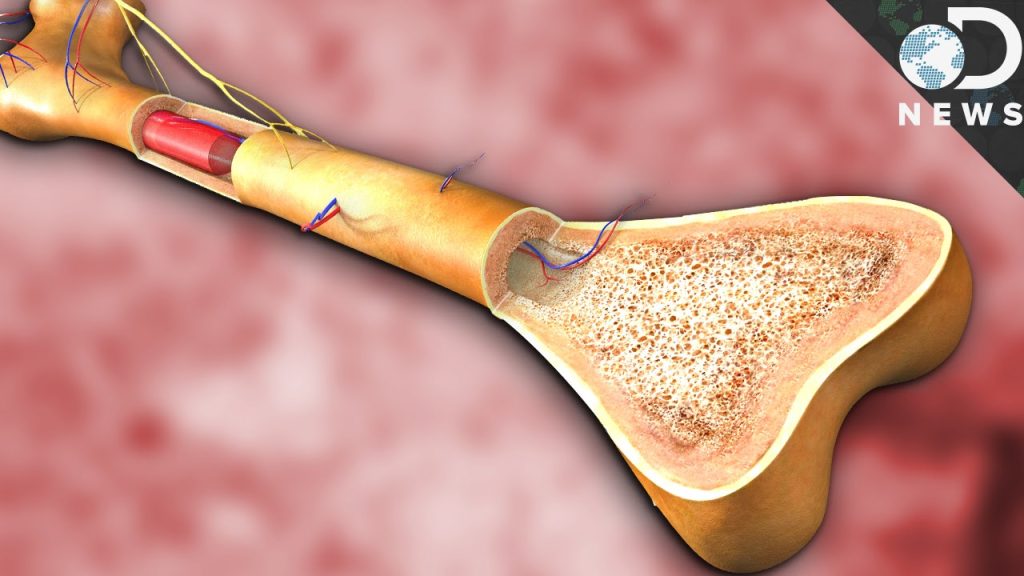
A bone marrow transplant is a medical procedure that involves replacing damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy stem cells. It is commonly used to treat various conditions, including certain types of cancer, blood disorders, and immune system deficiencies. However, the success rate of bone marrow transplants varies depending on several factors.
While bone marrow transplant can be a life-saving treatment, it is not always 100% successful. Success rates depend on factors such as the underlying condition being treated, the age and overall health of the patient, and the availability of a suitable donor. Additionally, complications can arise during and after the procedure, including infection, graft-versus-host disease, and organ damage.
Despite these challenges, advancements in medical technology and understanding have significantly improved the success rates of bone marrow transplants. According to the National Marrow Donor Program, the overall survival rate for patients who receive a bone marrow transplant is around 70-90%. This means that a significant majority of patients experience successful outcomes and regain their health.
In conclusion, while bone marrow transplant is not 100% successful, it remains a crucial and effective treatment option for many patients. Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to enhance success rates and improve the quality of life for those undergoing this procedure.
Can You Live a Healthy Life After a Bone Marrow Transplant?
Bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplants, are a medical procedure often used to treat various blood disorders, cancers, and immune system diseases. While the procedure can be life-saving, many individuals wonder if they can lead a healthy life after undergoing a bone marrow transplant.
The answer is yes, it is possible to live a healthy life after a bone marrow transplant. However, it is important to note that the recovery process can be lengthy and requires careful monitoring and follow-up care.
After a bone marrow transplant, patients may experience a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to infections. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain good hygiene practices and avoid exposure to individuals with contagious illnesses. Additionally, regular medical check-ups and blood tests are necessary to monitor the body’s response to the transplant and detect any potential complications.
Furthermore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for post-transplant health. This includes following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and managing stress levels. It is also important to adhere to any prescribed medications and attend all medical appointments.
In conclusion, while a bone marrow transplant can present challenges, with proper care and attention, individuals can lead a healthy life after the procedure. Regular medical follow-up, a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to medical advice are key to ensuring a successful recovery and long-term well-being.

Vimfay International Health Services