Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) is a rare and potentially life-threatening disease that has serious effects on the nervous system. This syndrome is characterized by damage to the nerves by the body’s immune system, leading to weakness, lethargy, and even paralysis. Guillain-Barre Syndrome can affect any age group and can progress rapidly. In this article we have written for you, we will explain the definition, causes, and symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
- What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- What Causes Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- What Are the Symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- How is Guillain-Barre Syndrome Diagnosed?
- How Is Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treated?
- What Are the Complications of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- Who Is More Likely to Get Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- What are the Latest Updates on Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
- When to Get Medical Help for Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- Recovering From Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treatment Prices in Turkey
What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
Guillain-Barre Syndrome is an autoimmune disease that affects the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that communicate with the rest of the body, depending on the central nervous system. GBS occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages these nerves. This leads to muscle weakness, loss of reflexes, lethargy, and reduced mobility. Rapid progression of Guillain-Barre Syndrome may cause patients to become unable to walk within a few days and in some cases require respiratory support.
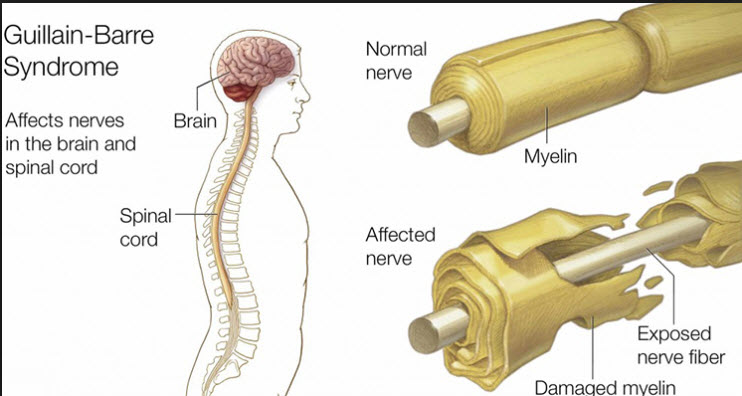
What Causes Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
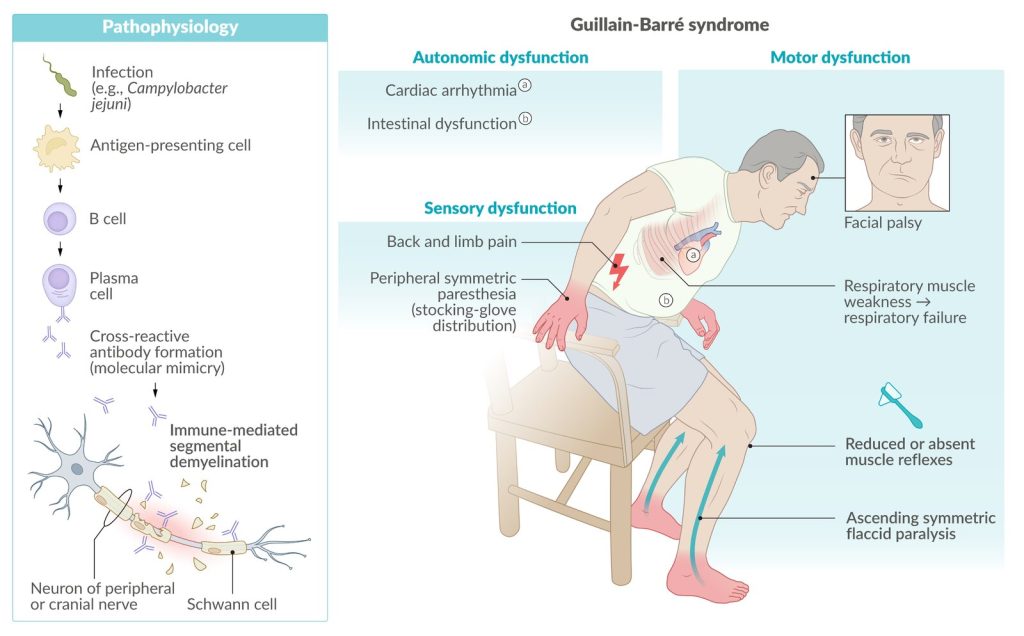
The exact cause of Guillain-Barre Syndrome is unknown. However, most cases of GBS are thought to be related to infections. These infections include bacterial infections (eg Campylobacter jejuni), viral infections (eg Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus) and even some vaccines. These infections can trigger a response that can cause the immune system to become hyperactive and damage nerves. It is also thought that certain genetic factors may increase the risk of GBS.
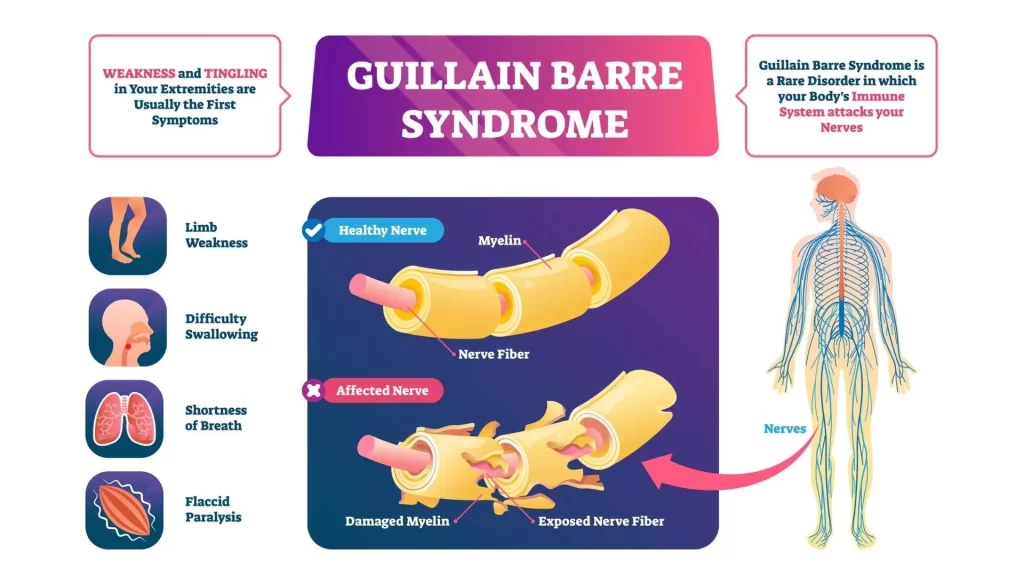
What Are the Symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
The symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome can vary from patient to patient, but they usually include the following symptoms;
- Numbness and tingling,
- Muscle weakness,
- Reflex loss,
- Coordination problems,
- Pain and cramps,
- Respiratory problems,
- Difficulty swallowing,
- Blood pressure and heartbeat changes
Guillain-Barre Syndrome is a disease that progresses rapidly and can lead to serious complications. Therefore, the quality of life of patients and the chance of recovery can be increased with early diagnosis of their symptoms and appropriate treatment.
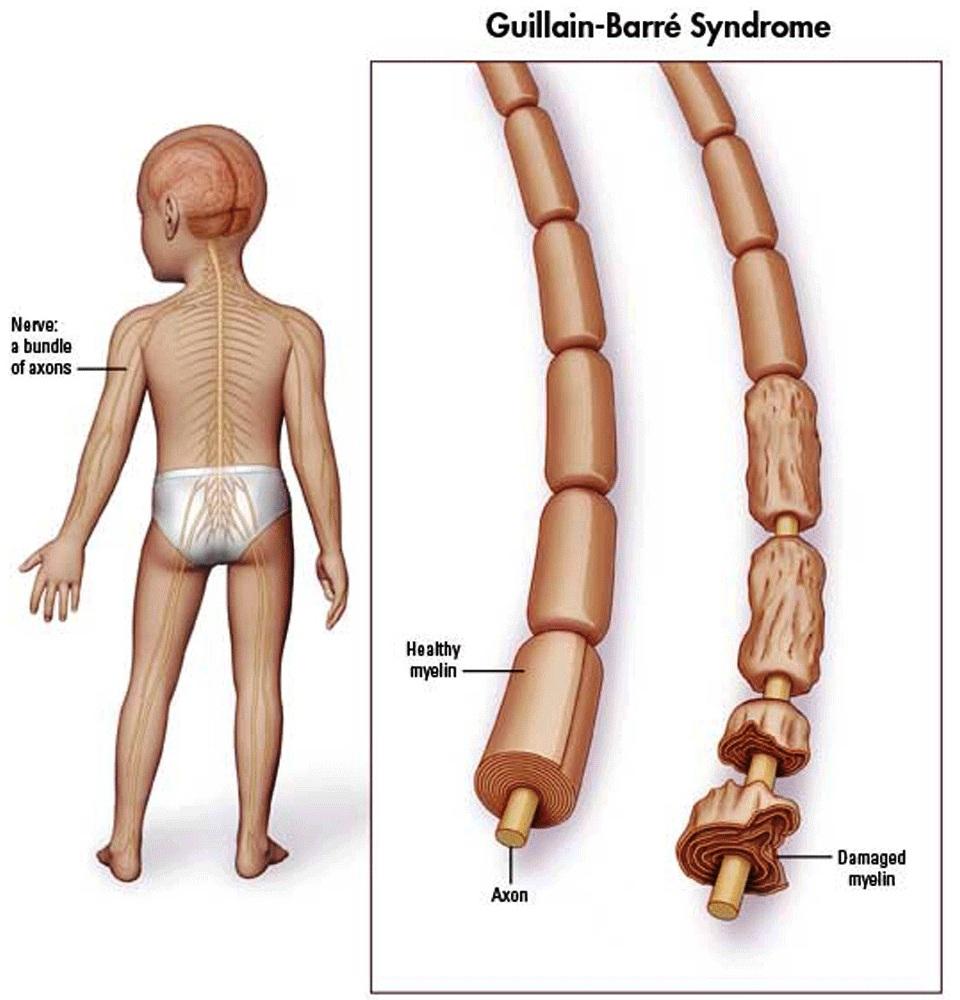
How is Guillain-Barre Syndrome Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of GBS is made by patients’ symptoms, physical examination findings, and some laboratory tests.
First, the patient’s symptoms are evaluated. GBS typically presents with weakness and tingling that begins in the hands and feet. These symptoms can spread quickly and lead to muscle weakness. Also, some patients may experience difficulty swallowing, vision problems, and breathing problems.
During the physical exam, the doctor usually checks the patient’s reflexes and muscle strength. In GBS patients, reflexes may be weak or absent and muscle strength may be decreased.
Laboratory tests also play an important role in the diagnosis of GBS. These tests may include:
Electromyography (EMG); This test measures how the muscles respond to electrical impulses. In GBS patients, the nerve conduction velocity is usually slow and can be detected with this test.
Nerve conduction studies; These tests measure how quickly nerves respond to electrical impulses. In GBS patients, the nerve conduction velocity may be slow.
Lumbar puncture (Cerebral spinal fluid analysis); During this procedure, the doctor takes a sample of cerebrospinal fluid with a needle from the lumbar region. In GBS patients, protein levels may be high in this fluid.
The diagnosis of GBS is made based on the results of these tests and the patient’s symptoms. However, it can be difficult to diagnose in the early stages of GBS, and in some cases, it may take time to fully diagnose the disease.
How Is Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treated?
Although there is no definitive cure for Guillain-Barre Syndrome, there are some treatment options to reduce the severity of the disease and prevent complications. GBS treatment is usually carried out in the hospital and the following methods can be used;
Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis); During this procedure, the patient’s blood is taken and the liquid part called plasma is cleaned. The cleaned plasma is then given back to the patient. This treatment helps remove harmful antibodies caused by GBS from the blood.
Immunoglobulin therapy; This treatment includes a high dose of immunoglobulin, which contains disease-fighting antibodies produced by the immune system. Immunoglobulin therapy can help strengthen the immune system of GBS patients and reduce the severity of the disease.
Supportive treatments; Supportive treatments for GBS patients are geared towards preventing and treating complications such as breathing problems, difficulty swallowing, and feeding problems. These treatments may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech-language therapy.
What Are the Complications of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
Guillain-Barre Syndrome can lead to serious complications in some cases. These complications may include;
- Respiratory Failure,
- Heart and blood pressure problems,
- Deep vein thrombosis,
- Swallowing and feeding problems,
- Nerve damage and permanent weakness
Who Is More Likely to Get Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare but serious autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. While anyone can develop GBS, certain factors may increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and management of the condition. In this article, we delve into who is more likely to get Guillain-Barré Syndrome and what steps can be taken for prevention and treatment.
Previous Infections: Individuals who have recently experienced a bacterial or viral infection, particularly respiratory or gastrointestinal infections, are at a higher risk of developing Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Some infections associated with GBS include Campylobacter jejuni, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and Zika virus. The exact mechanism linking these infections to GBS is not fully understood, but it is believed that the immune response triggered by the infection may mistakenly attack the nerves.
Age and Gender: While Guillain-Barré Syndrome can affect individuals of any age, it is more common in adults than in children. The risk of developing GBS increases with age, with the highest incidence occurring in individuals over 50 years old. Additionally, some studies suggest that men are slightly more likely to develop GBS than women, although the reasons for this gender difference are not well-defined.
Vaccinations: While extremely rare, certain vaccines have been associated with an increased risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome. The most well-known example is the influenza vaccine, particularly the swine flu vaccine used during the 1976 influenza pandemic. However, it’s important to note that the overall risk of developing GBS after vaccination is very low, and the benefits of vaccination in preventing infectious diseases generally outweigh the risks.
Genetic Factors: Although Guillain-Barré Syndrome is not considered a hereditary condition, there may be genetic predispositions that influence an individual’s susceptibility to developing the disorder. Research suggests that certain genetic variations related to the immune system and nerve function may play a role in increasing the risk of GBS in some individuals.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), have been associated with an increased risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Additionally, individuals with a history of cancer, particularly lymphoma, may have a higher likelihood of developing GBS, possibly due to the immune system’s response to cancer cells.
While these risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing Guillain-Barré Syndrome, it’s important to remember that the condition remains rare, and most people exposed to the associated triggers do not develop GBS. Additionally, early recognition and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals affected by GBS.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms such as muscle weakness, tingling sensations, or difficulty with coordination, especially following a recent infection or vaccination, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. A prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical care can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and support recovery from Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
In conclusion, while certain factors may predispose individuals to Guillain-Barré Syndrome, the condition’s exact cause remains unclear in many cases. By understanding these risk factors and being aware of the symptoms, individuals and healthcare professionals can work together to effectively manage GBS and improve outcomes for those affected by this rare autoimmune disorder.
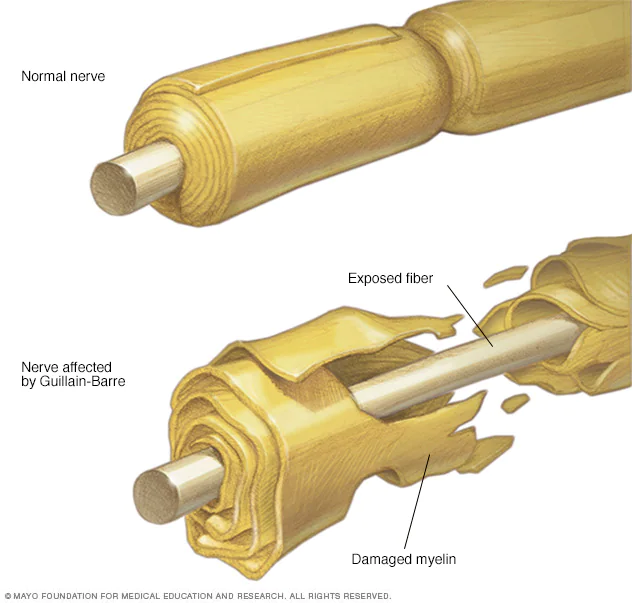
What are the Latest Updates on Guillain-Barré Syndrome?
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare but potentially serious neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. Keeping abreast of the latest updates and research findings on GBS is crucial for healthcare professionals, patients, and their families. In this article, we’ll explore the recent advancements and updates regarding Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
- Association with COVID-19: One of the most significant updates in the realm of Guillain-Barré Syndrome is its association with COVID-19. Research has shown that some individuals infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, may develop GBS as a complication. While the exact mechanism underlying this association is still being investigated, it highlights the importance of monitoring neurological symptoms in individuals with COVID-19.
- Treatment Strategies: Recent studies have focused on refining treatment strategies for Guillain-Barré Syndrome to improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) remain the mainstays of treatment for GBS, but research continues to explore novel therapeutic approaches, such as complement inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs, to target the underlying immune response more effectively.
- Genetic Factors and Biomarkers: Advances in genetic research have shed light on potential genetic predispositions to Guillain-Barré Syndrome and identified biomarkers that may help predict disease progression and response to treatment. By better understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms involved in GBS, researchers aim to develop personalized treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes.
- Long-Term Effects and Rehabilitation: While many individuals with Guillain-Barré Syndrome experience significant recovery with appropriate treatment, some may continue to face long-term neurological complications and disabilities. Recent research has focused on optimizing rehabilitation strategies and supportive care to help patients regain function and improve their quality of life following GBS.
- Vaccine Safety Monitoring: With the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines and other immunizations, ongoing surveillance and monitoring for potential adverse events, including Guillain-Barré Syndrome, are essential. Health authorities and regulatory agencies closely monitor vaccine safety data to identify any potential signals or trends suggestive of an increased risk of GBS or other neurological conditions following vaccination.
- Patient Support and Advocacy: In addition to scientific advancements, there has been a growing emphasis on patient support, advocacy, and community awareness initiatives for Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Patient organizations and support groups play a crucial role in providing resources, information, and peer support to individuals affected by GBS and their families.
In conclusion, staying informed about the latest updates and research developments on Guillain-Barré Syndrome is essential for healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers alike. From understanding the association with COVID-19 to refining treatment strategies and improving long-term outcomes, ongoing efforts in GBS research aim to enhance our understanding of the condition and optimize patient care. By remaining vigilant, advocating for patient needs, and fostering collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient communities, we can continue to make strides in the management and treatment of Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
When to Get Medical Help for Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare but potentially serious neurological condition that requires prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and management. Recognizing the signs and knowing when to seek medical help is crucial for ensuring timely intervention and optimizing outcomes. In this article, we’ll discuss when to get medical help for Guillain-Barré Syndrome and the key signs and symptoms to watch out for.
- Progressive Muscle Weakness: One of the hallmark symptoms of Guillain-Barré Syndrome is progressive muscle weakness, which typically starts in the legs and can spread to the arms and upper body. If you notice weakness or difficulty moving your limbs that seems to be getting worse over time, it’s essential to seek medical help promptly.
- Tingling or Numbness: Many individuals with Guillain-Barré Syndrome experience tingling sensations or numbness, often starting in the feet and hands and spreading inward. These sensory disturbances may be accompanied by pain or discomfort. If you experience unusual sensations that persist or worsen, especially if they affect your ability to walk or perform daily activities, it’s important to see a healthcare provider.
- Difficulty with Balance and Coordination: Guillain-Barré Syndrome can affect balance and coordination, leading to difficulties with walking, standing, or maintaining posture. If you find yourself stumbling, feeling unsteady on your feet, or experiencing coordination problems that interfere with your daily life, it’s advisable to seek medical evaluation.
- Breathing Difficulties: In severe cases of Guillain-Barré Syndrome, muscle weakness can extend to the muscles involved in breathing, leading to respiratory difficulties. If you experience shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or chest pain, seek immediate medical attention, as these symptoms may indicate a life-threatening complication requiring urgent intervention.
- Autonomic Symptoms: Guillain-Barré Syndrome can also affect the autonomic nervous system, leading to symptoms such as fluctuations in blood pressure, heart rate abnormalities, or bowel and bladder dysfunction. If you experience sudden changes in these bodily functions or symptoms suggestive of autonomic dysfunction, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
- Recent Infection or Vaccination: Guillain-Barré Syndrome is often preceded by a bacterial or viral infection, such as respiratory or gastrointestinal illness, or in rare cases, by vaccination. If you have recently had an infection or received a vaccine and subsequently develop symptoms suggestive of Guillain-Barré Syndrome, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation promptly.
In summary, if you experience any of the aforementioned signs or symptoms, especially if they occur suddenly or worsen rapidly, it’s crucial to seek medical help without delay. Guillain-Barré Syndrome requires prompt diagnosis and management to prevent complications and optimize outcomes. By acting quickly and seeking appropriate medical care, you can ensure timely intervention and receive the support and treatment you need to recover from Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Recovering From Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Recovering from Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) can be a challenging journey, but with patience, perseverance, and the right support, many individuals can regain function and improve their quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore key aspects of recovery from Guillain-Barré Syndrome and offer practical tips to help navigate the road to recovery.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery process for individuals with Guillain-Barré Syndrome. A tailored rehabilitation program, designed in collaboration with a physical therapist, can help restore strength, mobility, and coordination. Exercises focused on range of motion, muscle strengthening, and balance training can aid in regaining function and independence.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help individuals with Guillain-Barré Syndrome learn techniques and strategies to perform daily activities more independently. Occupational therapists can assist with tasks such as dressing, grooming, and household chores, as well as recommend adaptive equipment or modifications to facilitate participation in daily life.
- Speech Therapy: In cases where Guillain-Barré Syndrome affects facial muscles or swallowing function, speech therapy may be beneficial. Speech-language pathologists can help improve speech clarity, swallowing safety, and communication skills through targeted exercises and techniques.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for supporting recovery from Guillain-Barré Syndrome and maintaining overall health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, including protein, vitamins, and minerals, can promote muscle recovery and nerve function. It’s important to stay hydrated and consume adequate fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if swallowing difficulties are present.
- Pacing and Rest: Managing energy levels and avoiding overexertion is crucial during the recovery process. Pacing activities and incorporating rest periods throughout the day can help prevent fatigue and conserve energy for essential tasks. Listening to your body’s cues and taking breaks when needed is important for promoting healing and preventing setbacks.
- Emotional Support: Coping with Guillain-Barré Syndrome and its effects on daily life can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from family, friends, or a mental health professional can provide emotional support and guidance during the recovery process. Connecting with others who have experienced similar challenges through support groups or online communities can also offer valuable encouragement and understanding.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring progress, addressing any new symptoms or concerns, and adjusting treatment as needed. Open communication with your healthcare team ensures that you receive comprehensive care tailored to your individual needs throughout the recovery process.
- Gradual Return to Activities: As strength and function improve, gradually reintroducing activities and hobbies can help rebuild confidence and enhance quality of life. Start with low-impact activities and gradually increase intensity and duration as tolerated. Setting realistic goals and celebrating achievements along the way can boost motivation and morale.
In conclusion, recovering from Guillain-Barré Syndrome requires patience, perseverance, and a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation. By actively participating in physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other supportive interventions, individuals affected by GBS can make significant strides toward regaining function and independence. With the right combination of medical care, support, and self-care strategies, navigating the road to recovery from Guillain-Barré Syndrome is possible.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treatment Prices in Turkey
Turkey has succeeded in making its name known to the world with its investments and Especially the latest technological devices used in diagnosis and treatment procedures have been a beacon of hope for many diseases. However, there has been an increase in health tourism in Türkiye.
- Hospitals are large, clean, spacious and fully equipped in terms of technological equipment.
- Turkish doctors are specialized, successful, and skilled in their fields.
- Nurses and carers are friendly and compassionate.
- Finding answers to the questions asked quickly and accurately.
- Patience and understanding of all staff, including the intermediary company dealing with the patient.
- Turkey offers holiday opportunities with its natural and historical beauties.
- Easy transportation.
- Diagnosis, treatment, accommodation, eating, drinking, dressing, and holiday needs can be met at affordable prices.
Such situations are shown among the reasons for preference. Regarding Guillain-Barre Syndrome Treatment Prices in Turkey, we can see that patients and their relatives who want to come to Turkey are doing research. However, it would not be correct to give clear price information at this stage. Many factors such as the type of disease, stage, diagnosis process, treatment process, and stay in Türkiye affect the price issue. If you want to get more detailed price information, you can contact us. In addition, if you come to Turkey for treatment through us, we can facilitate your visa application process with the invitation letter sent by us to the consulate.

Vimfay International Health Services