The field of general surgery is the branch of medicine that provides the removal or surgical treatment of the organ in diseases that cannot be treated with medication. In the field of general surgery, obesity surgery, endocrine surgery, digestive system organs surgery, liver and gallbladder surgery, pancreatic surgery, and breast surgery are frequently performed. In this area, surgeries related to every system in the human body can be performed. Therefore, the field of general surgery works together with specific fields that examine each system. General surgeons should cooperate with specialties such as internal medicine, gastroenterology, gynecology, oncology, thoracic surgery, cardiovascular surgery, bariatric surgery, and endocrinology, depending on the organ of the disease. In the field of general surgery, thyroid diseases, stomach problems, intestinal diseases, hemorrhoids, ingrown hairs, inguinal hernias, abdominal hernias, anal fistulas, liver, and pancreas diseases are treated.
Transplantation Surgery (Organ Transplantation)

Transplantation surgery (organ transplant) is an operation performed to remove an organ from a body and replace it with another organ. The donor body and the recipient body can sometimes be the same. In addition, the donor body can be alive or cadaver.
Today, the most frequently transplanted organs can be listed as kidneys, liver, heart, pancreas, lungs, and uterus. The factor that determines the success of transplantation surgery is whether the transplanted organ causes an immune response in the recipient body. For a successful transplant surgery, the match between the donor and the recipient must be suitable. In some cases, immune responses that may occur with the use of drugs that suppress the immune system can be prevented.
Several types of transplantation surgery vary according to the characteristics of the recipient. Autograft is when the recipient and donor are in the same body. For example, skin grafts made after burns, and vascular grafts used in bypass surgeries are taken from the individual’s own body and placed where needed. In addition, in some surgeries performed on the extremities, the removed joint is placed in another joint, and surgery is performed. The foot and ankle joint, which is often removed, is placed in the place of the knee joint. An allograft is when the donor and recipient are different bodies of the same species. The donor can be a living human body, a brain-dead patient, or a cadaver. The biggest problem that can be encountered in cases where allograft is applied is the rejection of the tissue by the recipient body. A xenograft is when the donor and recipient are of two different species. Pig heart valve transplant surgery can be given as an example of transplantation from different types of donors to humans today.
Today, some organs and tissues and donor types that have been successfully transplanted have been identified. Heart transplantation can be performed from both a cadaver and a living donor. Lung transplantation is performed only from a cadaver donor. Stomach, pancreas, and penis transplantation can only be performed from a cadaver donor. Kidney, testis, and bone transplantation can be performed from both living and cadaveric donors. Blood vessels and bone marrow transplantation can be achieved by autograft or by a cadaver donor.
Tissue and organ donation can be made by anyone. If an individual who has brain death has donated an organ, the donor body can be kept under appropriate conditions until the transplant process takes place. For organ transplantation, it is aimed that the organs of the individual whose circulation and respiratory functions are maintained depending on the machine do not suffer from loss of function. Such a procedure is generally not required for tissue transplantation. Most tissues (except the cornea) can be preserved for graft by being stored under appropriate conditions after being removed from the living body.
Endocrine Surgery
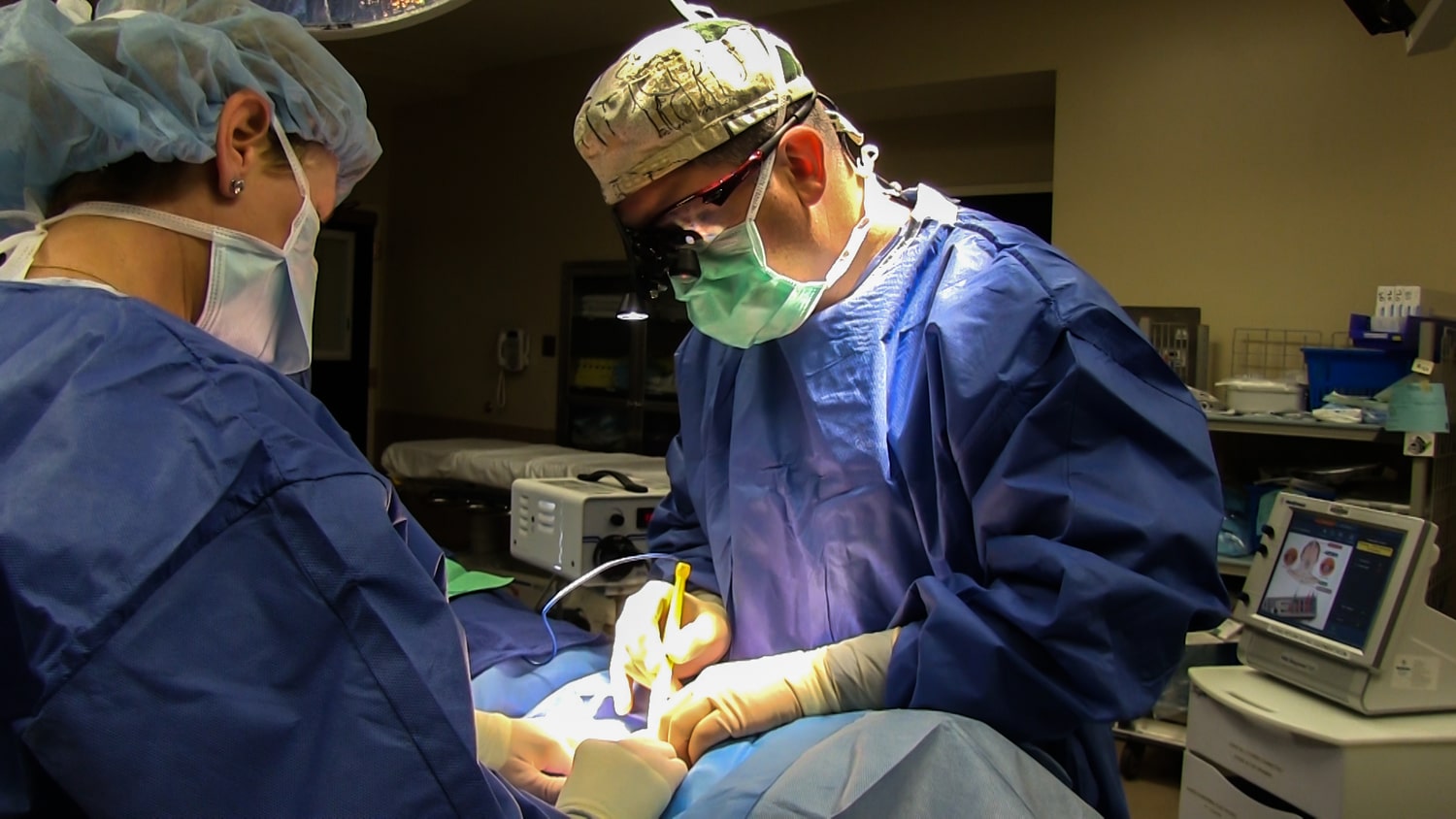
The field of endocrine surgery aims to treat diseases of the endocrine glands (thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal gland) in our body. Surgery is performed for diseases such as goiter, thyroid cancers, and thyroid nodules belonging to the thyroid gland. Surgery is performed for the parathyroid gland in cases of parathyroid cancers or overworking of the gland (hyperparathyroidism). Surgery is performed in cancers of the adrenal gland (adrenocortical cancers), and diseases involving the adrenal gland such as Addison’s and Cushing’s Syndrome. Pancreatic diseases involving the endocrine part of the pancreas (insulinoma, gastrinoma, carcinoid syndrome, etc.) can also be treated with endocrine surgery.
Goiter surgery is a surgical method that is frequently used in the treatment of the thyroid gland. Indications for surgery can be listed as enlargement of the thyroid gland, making breathing difficult, presence of nodules suspected of cancer in the thyroid gland, and patients with goiter who cannot use medication. In goiter surgery, the intervention is performed with a small incision made from the front of the neck. Nodules on the thyroid gland can be cleaned and removed, or the entire gland can be removed. The most common postoperative complication is hoarseness experienced by patients. During the operation, the nerves that enable the vocal cords to work can be partially damaged because they travel very close to the thyroid gland. The risks of such complications are minimized in surgeries performed by experienced surgeons. The drain at the patient’s incision site is usually removed at the end of the first day after surgery. Patients can be fed orally after the necessary evaluations are made. Patients who have their entire thyroid gland removed must use a drug that takes over the function of the thyroid gland throughout their lives.
Cushing’s Syndrome is a disease that develops due to the adrenal gland producing more than normal cortisol hormone. Cushing’s syndrome findings can be listed as obesity, buffalo hump, moon face, pink skin appearance, abdominal skin cracks (striae), amenorrhea in women (absence of menstruation), depression, hypertension, and insulin resistance. In the treatment of this disease, medical therapy is usually applied to reduce cortisol to normal levels. Surgical treatment can also be applied to patients who cannot be cured by drug therapy. The surgical method to be applied varies according to the main cause of the disease. If the disease has developed due to an adenoma in the pituitary gland, the adenoma is removed by pituitary surgery and treated. If the disease has developed due to overwork of the adrenal gland, a surgical operation can be performed to remove the adrenal glands.
Gallstones Surgery
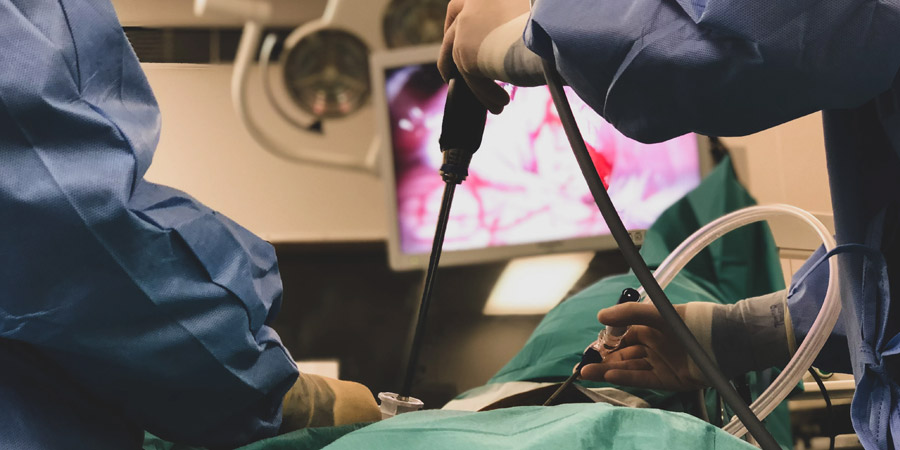
The gallbladder is a hollow organ located under the liver. The task of the gallbladder is to act as a sac to store the bile secreted by the liver. Bile secreted by the liver has a role in the digestion process of the fats we take with food. Bile stored in the gallbladder between meals during the day is transferred to the intestine by the contraction of the gallbladder. Thus, the digestion process is carried out. However, some substances in the bile accumulated in the gallbladder precipitate during storage and cause formations with a thick consistency similar to mud.
These substances, which are formed as a result of precipitation, can turn into gallstones over time. There are no symptoms during the formation of gallstones. For this reason, gallstones may sometimes be discovered incidentally during radiographic examinations performed for another problem. Untreated stones, on the other hand, may pass into the bile duct in the gallbladder over time, preventing both the flow of bile and the secretions of the pancreas. Symptoms begin to appear after the stones formed in the gallbladder pass into the bile duct. The most obvious of these symptoms is a type of pain specific to biliary problems. This pain is a type of pain in the right part of the abdomen that starts suddenly after meals, increases, and goes away on its own over time. In addition to these, symptoms such as nausea and intense sweating may also occur. Diagnosis of gallstones is made by clinical examination and radiographic examination in addition to the patient’s history.
The most common method for removing stones after diagnosis is gallbladder removal surgery. In some cases, surgery may not always be performed directly. The patient may experience an infection or jaundice due to a problem in the bile Infection in the bile can even reach the pancreas and cause pancreatitis. In such cases, attempts can be made to open the bile duct to stabilize the patient’s condition before surgery. With these interventions, the patient’s values are expected to return to normal with drug treatment after the bile duct is opened. After the values return to normal, surgery can be performed to prevent the recurrence of bile duct obstruction. The surgery is mostly performed in a closed manner. The patient is treated by removing the gallbladder with the help of a video camera.
Mostly, patients do not encounter any other complications and are discharged on the same day. Open surgeries may take a little longer to recover or discharge depending on the condition of the disease. It is important to make changes in the diet after gallbladder surgery to facilitate digestion. Concerning bile, foods with high-fat content should be avoided as much as possible. Especially after surgery, this type of nutrition should be avoided and this type of food should be started gradually. Apart from staying away from a fatty diet, it is beneficial to consume foods with high fiber content. In addition, it is useful to do breathing exercises after this type of abdominal surgery. Superficial breathing sometimes develops in patients due to the surgery performed in the abdominal region. Breathing exercises are of great importance in preventing this.