Physiotherapy and rehabilitation, treatment of functional disorders caused by various musculoskeletal system, nervous system, cardiovascular system, pulmonary system (respiratory system) disorders, reducing the pain of individuals, increasing their participation in daily life activities, It is the area of expertise that ensures the restoration of balance and the protection of the individual’s place in society. The field of physical therapy and rehabilitation is divided into systematic sub-branches such as orthopedic, neurological, pediatric, rheumatological, cardiopulmonary, obstetric and urogynecological, and rheumatological physical therapy and rehabilitation. In addition, there are sub-branches such as hand and spine rehabilitation covering anatomical body parts where injuries are common. The most commonly used physical therapy and rehabilitation methods in the treatment and prevention of diseases are heat-light-water agents, electrotherapy, manual therapy, mechanotherapy, therapeutic exercises, home exercises, daily life changes, assistive devices, and orthosis-prosthesis use.
Orthopedic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
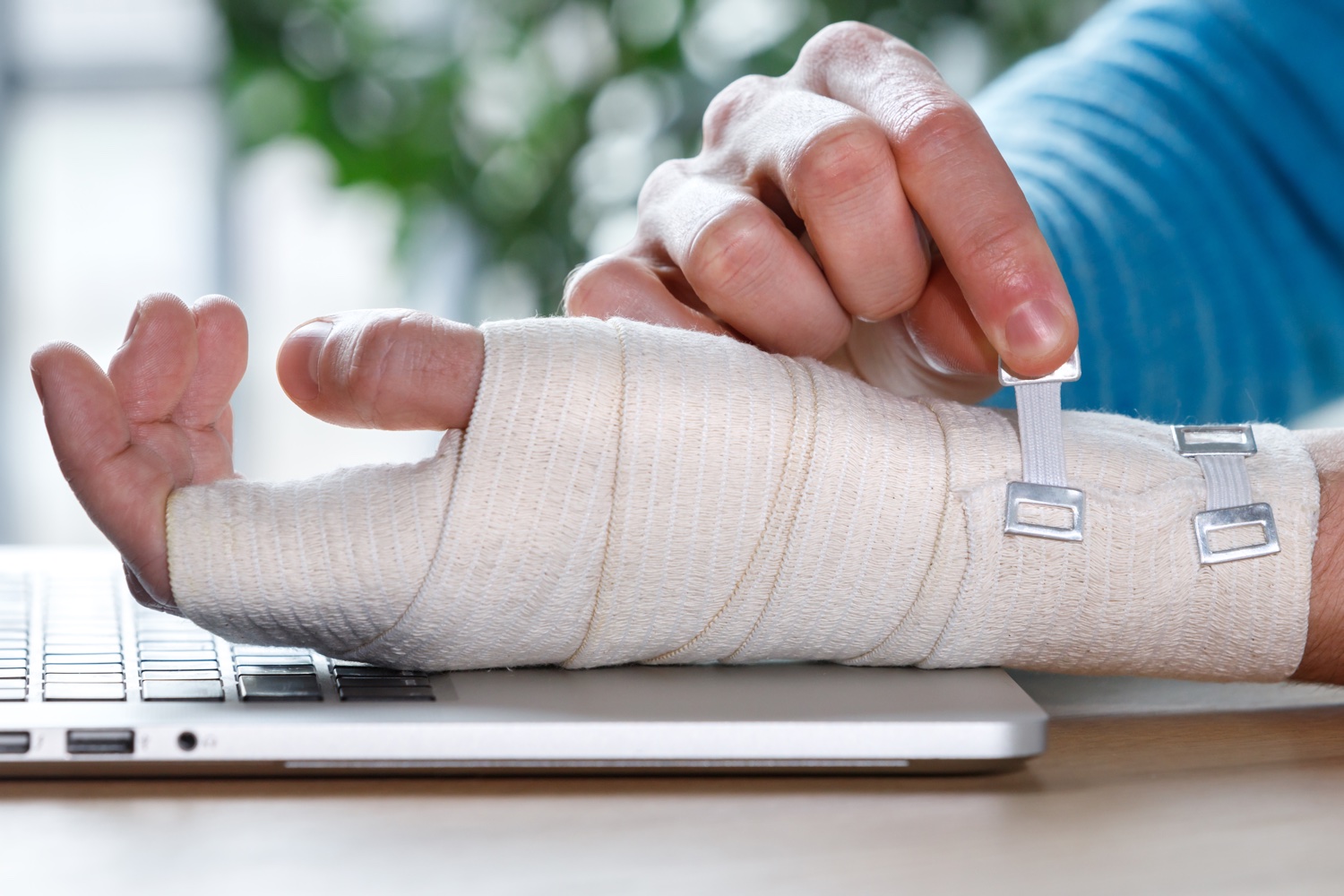

Orthopedic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy applied in the treatment of various musculoskeletal diseases, before (pre-operatively) surgical interventions planned to be applied for these treatments, and after surgical interventions (post-operative) to regain lost functions.
In the field of Orthopedic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation, ankle sprains, bursitis, tendinitis, lumbar and neck hernia, calcification (osteoarthritis), flat feet (pes planus), hallux valgus, carpal tunnel syndrome, muscle tears, scoliosis, nerve compression (trap neuropathies) Approaches to the treatment of diseases such as tennis elbow (medial epicondylitis), golfer’s elbow (lateral epicondylitis), myofascial pain syndrome (trigger point), a heel spur (calcaneal epin) and torticollis are carried out. These diseases, in most cases, cause strain on the joints, deterioration of proper alignment, injury to the formations and muscles around the joint, and in some cases, compression of the nerves located near the joint and inflammation in the following processes, due to excessive use of a joint or forcing it out of its function.
Physical therapy applications aimed at curing diseases or reducing the symptoms seen during the active period include electrotherapy, the use of various dry or moist heat agents, manual therapy, massage, and therapeutic exercise approaches. Electrotherapy agents can be used to reduce the patient’s pain complaint (analgesic) or to restore the strength of the weak muscles, depending on the type and intensity of the preferred electric current. Electrotherapy is a painless, easy, and risk-free method as it is applied to the body through currents that have been tried and proven effective before. Dry or moist heat agents provide acceleration of metabolic activities and regulation of circulation in the area where it is applied. While the cold application is applied to control edema, which is usually seen in acute injuries, the hot application is applied to reduce pain and relax muscles in chronic cases. Manual therapy and massage applications are one of the important steps of the physical therapy and rehabilitation process and can only be applied by trained health personnel. Manual therapy and massage applications are performed to restore the range of motion of the injured area, relax the spasm or stiffen muscles, and increase circulation. Therapeutic exercise approaches are effective methods for gaining the patient’s required range of motion and increasing muscle strength. All exercises necessary for the patient’s clinical visits are performed under the supervision of experts, using auxiliary equipment (strength bands, weights, pilates balls, etc.). In addition to these, an exercise prescription is created for the patient to apply himself at home. The exercise prescription is regularly revised according to the patient’s strength level during the rehabilitation process. In the whole physical therapy and rehabilitation process, the patient needs to participate in the exercises, learn the exercises correctly and apply them at home.
Neurological Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
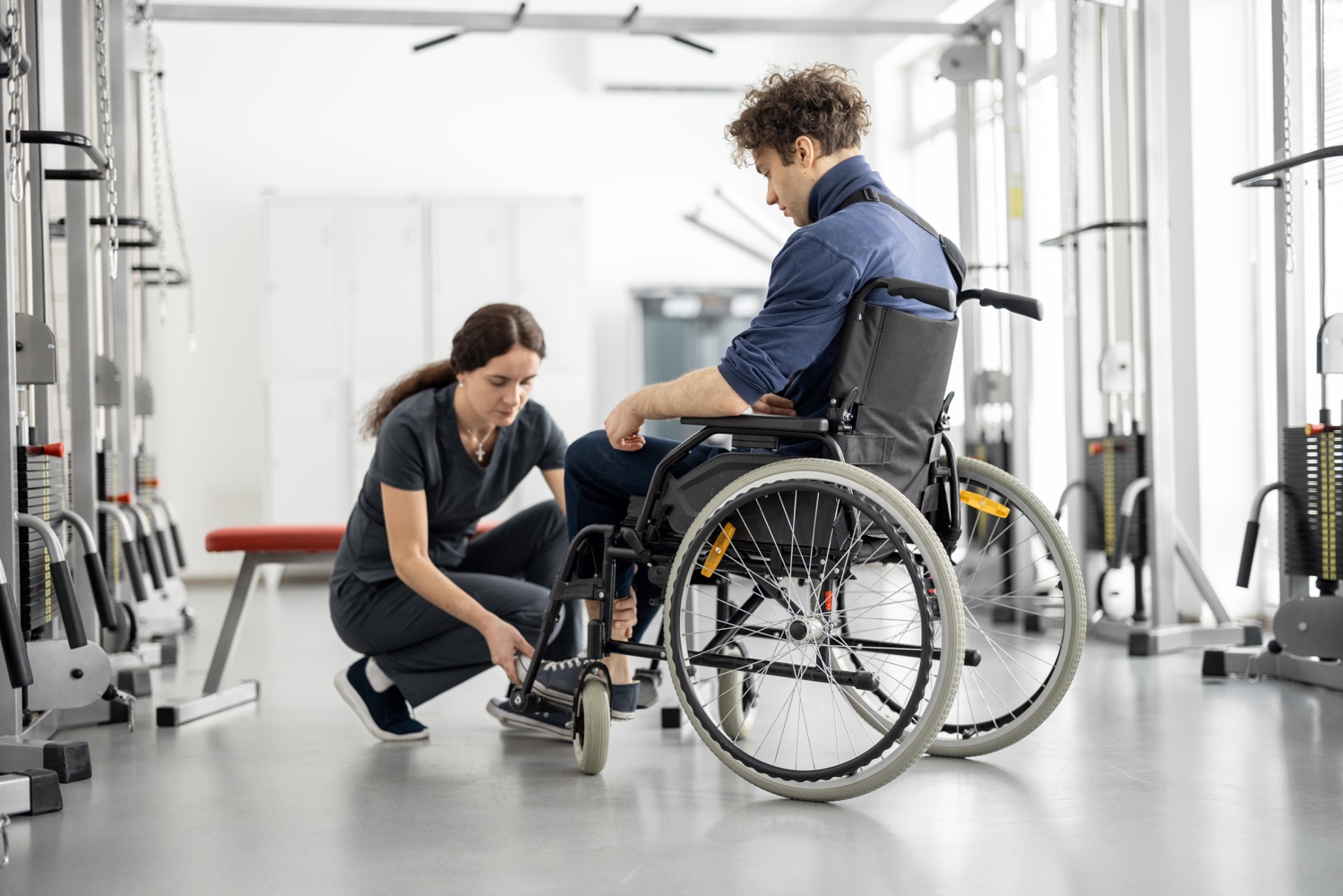

Neurological Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy applied for the treatment of disorders that occur as a result of various nervous system diseases in the acute and chronic periods, including different targets.
In the field of Neurological Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation, approaches are often carried out for the treatment of diseases such as stroke (hemiplegia), multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries (paralysis), muscle diseases (neuromuscular diseases).
Stroke, according to the definition of the World Health Organization; is a clinical picture that progresses with the rapid establishment of signs of regional brain dysfunction without any apparent reason other than vascular causes. troke occurs in cases of bleeding into the brain tissue (hemorrhage) or interruption of the cerebral blood flow (ischemia) depending on the problems in the brain vessels.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system characterized by myelin (nerve sheath) and nerve damage. The most common symptoms are optic nerve involvement, sensory and motor disorders, brain dysfunction, and bladder bowel problems. The physical therapy and rehabilitation applications needed from the initial period to the advanced period vary and are revised throughout the process.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system. The most common findings related to this disease are tremor, stiffness (rigidity), slowing of movements (bradykinesia), freezing (akinesia), and flexion posture. The rehabilitation process is aimed at protecting the existing functions of the person in the best way and maintaining the range of motion in his joints for a long time.
Spinal cord injuries can develop due to many traumatic or non-traumatic causes. Following spinal cord injury, motor, sensory and autonomic functions are impaired, leading to many accompanying secondary problems. Special rehabilitation programs are planned for problem-solving so that individuals with spinal cord injuries can lead a productive and independent life after the injury.
Muscle diseases (neuromuscular diseases) are inherited or acquired diseases that affect motor cells, peripheral nerves, neuromuscular junctions, or the muscle itself. The most prominent findings of this group of diseases are progressive loss of muscle strength, fatigue, pain, decrease in exercise capacity, difficulty in relocation (transfer activities), and weight problems. The physical therapy and rehabilitation process is aimed to increase functional capacity, to protecting independence and quality of life in daily living activities.
Pediatric Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
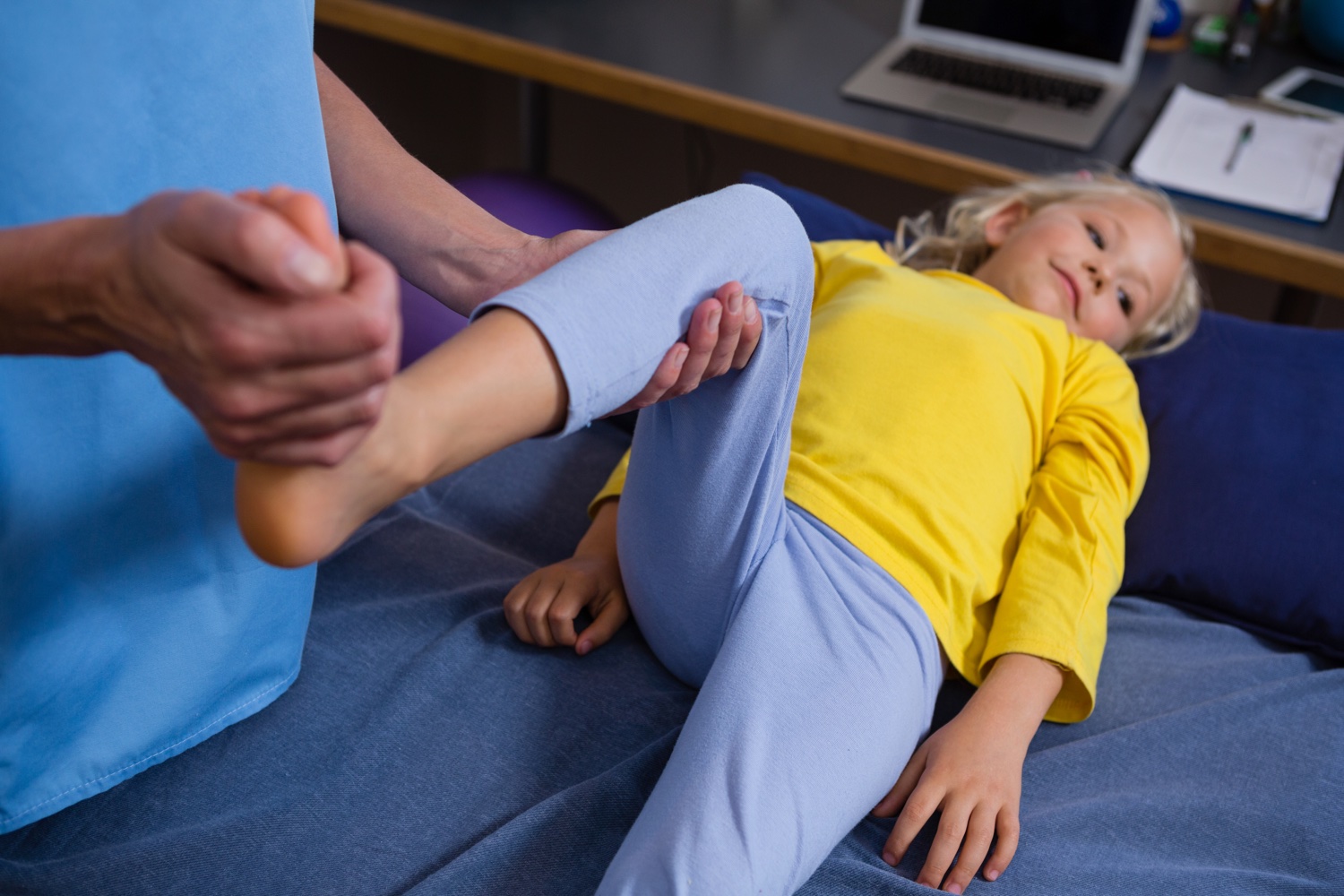
Pediatric Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy applied to regain functional independence in children with congenital or acquired neurological and orthopedic problems.
The most common diseases in the field of pediatric physical therapy and rehabilitation are cerebral palsy (CP), pediatric neuromuscular diseases, obstetric brachial plexus paralysis, and spina bifida.
Cerebral palsy is defined as a group of permanent movement and posture changes that cause activity limitations due to disorders in the developing fetal and newborn brain. The most common findings in children with this disease are contractures, torsional deformities, hip dislocation, spinal deformities (scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis, etc.), spasticity, muscle weakness, and epileptic disorders.
Pediatric neuromuscular diseases are mostly genetically inherited, have anatomically different involvements, and progress with progressive and widespread muscle weakness. In these diseases, postural disorders such as scoliosis in the spine and involvement of proximal muscle groups (hip and shoulder muscles) are frequently observed. General goals in physiotherapy and rehabilitation can be listed as prevention of muscle shortness, protection of gait, protection of respiratory functions, prevention of scoliosis, and prevention of progression if scoliosis has developed.
Obstetric brachial plexus paralysis is a clinical picture that develops due to injury at any level of the nerves going to the baby’s upper extremity during delivery. In this picture, varying degrees of paralysis are often seen in different parts of the upper extremity. The physiotherapy and rehabilitation program consists of a wide spectrum ranging from family education to sensory regulation, orthoses to protect muscle tissue and joints, stretching and strengthening exercises, and the use of various agents for spasticity.
Spina bifida is one of the types of congenital neural tube defects that occur due to developmental abnormalities of the bone and neural elements of the spine. Hydrocephalus, paraplegia (paralysis in both lower extremities), and incontinence are frequently seen in neural tube defects. Treatment procedures vary according to the level of motor loss in the rehabilitation process of the disease. While it is aimed to protect and develop the existing lower extremity muscle strength in patients who can walk, it is aimed to strengthen the upper extremity in patients using wheelchairs, and to reach the functional capacity where the patient can perform his/her transfer and activities of daily living independently.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation methods suitable for the disease in children are decided by considering the chronological age, neurodevelopmental status, age of onset of physiotherapy, physical disability and cognitive impairment, hearing and visual impairments, and general health status of the child.
Rheumatologic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
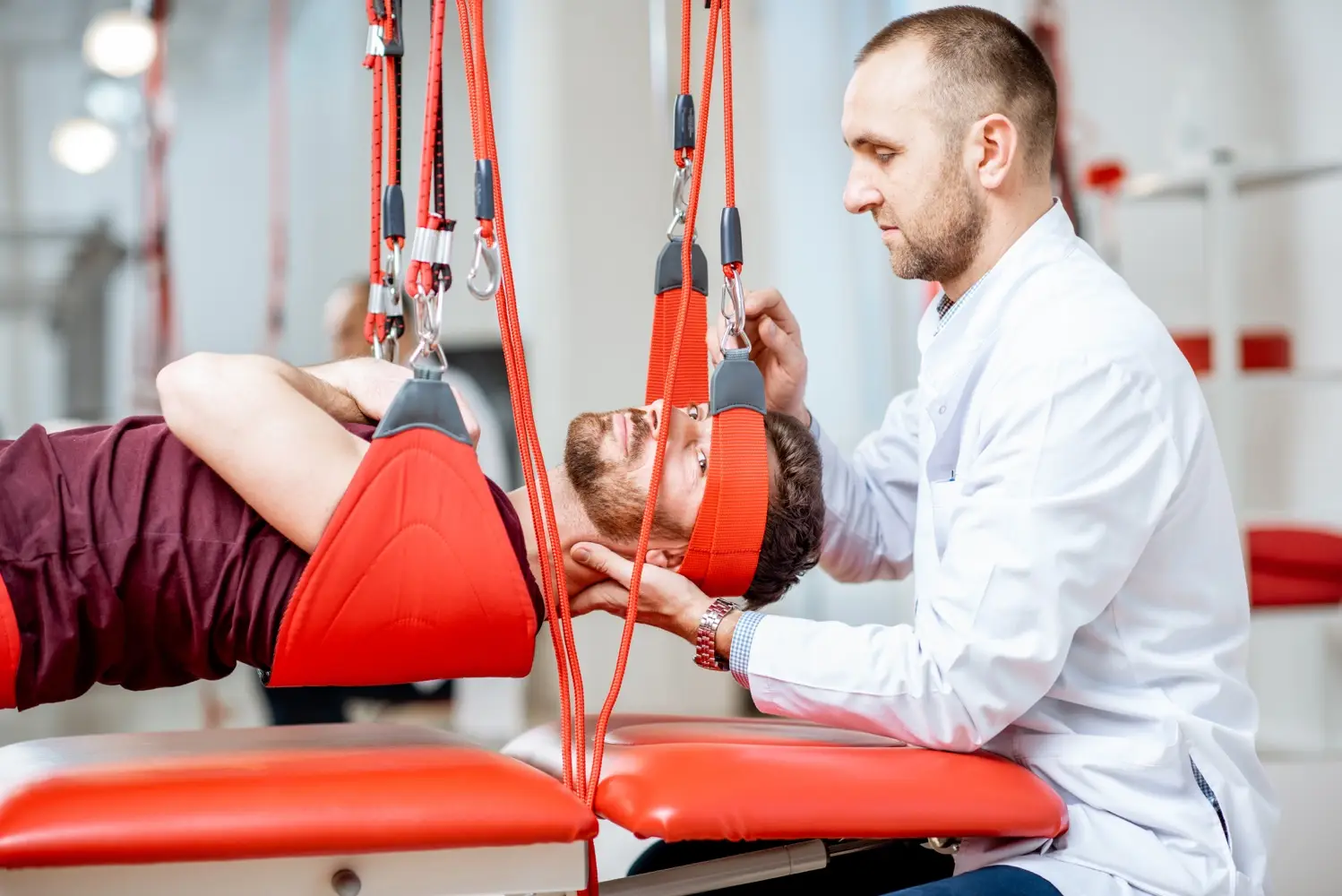

Rheumatologic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy applied to control inflammation, reduce pain and increase functionality in diseases caused by inflammatory processes occurring in the musculoskeletal system.
The most common diseases in the field of rheumatologic Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation are rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. These diseases are generally defined as progressive, systemic and chronic diseases of unknown cause, affecting the synovial joints.
Although rheumatoid arthritis is mainly known as a joint disease, it is also characterized by extra-articular systemic manifestations. It is most common between the ages of 20 and 50 and the incidence of the disease increases with age. Recent research points to a genetic basis for the development of rheumatoid arthritis. The characteristic onset is insidious pain, prolonged morning stiffness in the joints and symmetrical swelling of the small joints (joints of the hands). Often the first systemic manifestations are fatigue, weakness, weight loss and high fever. Joint involvement leads to buttonhole and swan neck deformities in the fingers in the advanced period. In addition, the disease may be accompanied by elbow joint limitation, shoulder joint dislocations, knee joint effusion, pain with movement in the hip joint and loss of movement in the cervical region of the spine. The short-term goals of the physical therapy and rehabilitation program to be applied to rheumatoid arthritis patients are to reduce the patient’s pain, prevent new deformities and give the patient the habit of exercising. Long-term goals are to increase the patient’s flexibility, strengthen atrophic (weakened) muscles and enable the patient to participate in activities. Patients are recommended orthoses and splints for night use after the necessary evaluations.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic progressive inflammatory disease that often involves the vertebrae and sacroiliac joint, and also shows extra-articular manifestations. Patients often present to the clinic with low back pain that has lasted for at least three months, improves with exercise, but does not improve with rest. There is also restricted movement of the lumbar vertebrae. The disease most often starts between the ages of 15 and 30. The pain increases in the morning and decreases with warm application and exercise. One of the characteristic findings of ankylosing spondylitis is enthesitis. Enthesitis is an inflammatory condition where ligaments and tendons attach to the bone. Patients may also experience respiratory failure due to enthesitis of the thoracic joints. The physiotherapy and rehabilitation program to be applied aims to increase spinal mobility, reduce pain, increase general muscle strength and prevent complications that may develop in the structures around the joint (such as nerve compression, etc.). For this purpose, electrotherapy applications, hydrotherapy, exercise and massage applications are used.
Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation

Pulmonary Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is the branches of physical therapy applied to individuals with a chronic respiratory disease whose symptoms persist despite medical treatment, while Cardiac Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is the branches of physical therapy applied to individuals with chronic cardiovascular disease. The approaches applied in these areas aim to optimize the physical, psychological, and social conditions of those with cardiopulmonary disease and to slow the progression of the disease.
Indications for cardiac rehabilitation can be listed as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), stable angina pectoris (chest pain), coronary artery bypass graft surgery, heart valve repair or replacement, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, heart transplantation, and heart-lung transplantation. Cardiac rehabilitation starts from the period the patient spends in the hospital after the operation and includes 3-6 months after discharge. The rehabilitation program mostly includes exercise training, gaining regular physical activity habits, and quitting smoking. In addition, since diabetes and hypertension are very common among patients who need cardiac rehabilitation, the rehabilitation program is planned to include these diseases.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is practiced in most patients with pulmonary activity limitations, such as those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a lung disease characterized by progressive airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. It often develops as a result of the inflammatory process that occurs against exposure to cigarette smoke or different harmful gases. The rehabilitation program aims to maximize the patient’s exercise performance, increase participation in daily activities and reduce the systemic effects of the disease. Pulmonary rehabilitation can be performed on an outpatient basis, as well as for inpatients before and after transplantation surgery, in restrictive lung diseases and diseases such as pulmonary hypertension.
Cardiopulmonary rehabilitation programs usually begin with patient education, lifestyle changes, and control of respiratory infections. Then, relaxation techniques, respiratory control methods, active breathing techniques cycle, bronchial drainage techniques, coughing training to ensure bronchial cleansing, respiratory muscle training, postural drainage, and stretching exercises to increase rib cage mobility are added to the program and the process is managed.
Cardiopulmonary rehabilitation is a program applied to patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit in addition to the diseases mentioned above. Existing diseases of the patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit are frequently caused by decreased volume in the lungs, respiratory muscle weakness, clearance of secretions (sputum), acute respiratory failure, decreased mobility and insufficiency in physical functions, etc. accompanied by clinical problems.
Obstetric-Urogynecological Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation

Obstetric-Urogynecological Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy that includes treatment methods that are often applied in cases of urinary incontinence and fecal incontinence (feel incontinence).
Urinary and fecal incontinence are serious health problems that cause the individual to be isolated from social environments and negatively affect their quality of life. There are subtypes of urinary incontinence:
Urinary stress incontinence: Urinary incontinence is seen during activities such as coughing, sneezing, and heavy lifting due to weakness in the pelvic floor muscles.
Urge type incontinence: Urinary incontinence that occurs in the form of expulsion of urine with a strong desire to empty. It is also called an overactive bladder.
Overflow type incontinence: It is urinary incontinence that develops due to excessive stretching of the bladder.
Nocturnal incontinence: Incontinence during sleep.
It is very important to evaluate the patients before the physiotherapy and rehabilitation program is applied for incontinence. The evaluation phase in incontinence includes taking the history, physical examination, and neurological examination. Frequency/volume chart, pad test, pelvic floor muscle strength assessment, visual analog scale, and quality of life questionnaires are applied specifically to urinary incontinence patients. Bowel habit diary, food diary, recto-anal examination, and quality of life questionnaires are applied specifically to fecal incontinence patients.
The physiotherapy and rehabilitation program applied in case of urinary incontinence includes many methods aimed at retraining the pelvic floor muscles and bladder. Bladder training is given to patients who go to the toilet at every opportunity, especially to avoid incontinence. With training, it is tried to delay the time to go to the toilet from 2 hours to 4 hours. Pelvic floor muscle training is provided by pelvic floor exercises performed in different positions. First, sitting in a chair, arms are supported on the knees, and legs are slightly spread to the side. After the achievement of the exercise in the sitting position, pelvic floor exercises are performed in the standing position and then in more dynamic situations. With these exercises, urinary incontinence can be prevented by increasing both the strength and endurance (contraction times) of the pelvic floor muscles.
The physiotherapy and rehabilitation program applied in case of fecal incontinence includes behavioral therapy, anal sphincter exercises, anal manometer application, and electrical stimulation. The main purpose of the applications is to prevent involuntary stool output by increasing the contraction force of the pelvic floor muscles and anal sphincter.
Hand Rehabilitation

Hand Rehabilitation is a branch of physical therapy and rehabilitation that includes the treatment of common injuries in the hand and wrist area. The most common injuries in this area are flexor tendon injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, and hand fractures.
Flexor tendon injuries are injuries that often affect the young and working population and cause significant limitations. Rehabilitation in tendon injuries usually begins after surgery. The rehabilitation procedure varies according to the level of injury and the type of injury. Healing after glass and knife cuts has a better prognosis than splinter injuries. In the early stages of rehabilitation (0-4 weeks), approaches that protect the tendon are exhibited. In the middle period (4-8 weeks), the protective approach is replaced by increasing tension on the tendon. In late rehabilitation (8 weeks and later), the tension applied to the tendon is increased and resistance exercises are started. Blocking exercises, tendon gliding exercises, place and hold exercises, and resistance exercises are frequently used in the rehabilitation of tendon injuries.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is defined as the findings due to compression of the median nerve in the wrist between the tendons. The causes of the disease include excessive use of the hand during the day, exposure of the hand to a load above its capacity (such as carrying heavy items), repetitive movements involving the wrist and hand (such as cleaning, dishwashing), and not taking rest breaks among all these functions. Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome usually experience pain, numbness, tingling, etc. radiating to the inner part of the palm and thumb, index, and middle finger. has complaints. In addition, patients have complaints such as decreased hand strength, not being able to hold items in their hands for a long time, not being able to open bottle caps, not being able to open the tap, and not being able to turn a key. In mild and moderate patients, the use of the hand during the day is reduced by the use of rest and night orthosis. Advanced patients require surgical treatment followed by a physical therapy program. The goals of rehabilitation are to reduce tenderness and pain, prevent deformity and permanent damage, prevent re-injury with training, provide a normal joint range of motion, and prevent post-surgical immobile scar tissue formation. The applied physical therapy and rehabilitation program includes the strengthening of the affected muscles, the use of electrotherapy and analgesic agents to reduce pain, and the proper positioning of the hand (use of orthosis).
Spine Rehabilitation

Spinal problems can be related to structural, psychosocial, biomechanical, and neurophysiological factors. Most patients can recover with minimal functional and lifestyle changes that prevent the emergence of the behavior that causes the spine problem, which can be discussed under the heading of psychosocial factors. Although structural factors are not the underlying cause of most spinal pain, this does not mean that all pain is functional or psychogenic.
Inadequate function of the locomotor system, especially poor motor control, is closely related to spinal problems. Rehabilitation of patients with spinal problems is based on understanding how the spine is injured, how the spine responds to pain or injury, and how it can be stabilized. Spine and whole-body stability are two different but related phenomena. Whole-body stability; the body can maintain balance after being exposed to external forces that temporarily destabilize it. The spine, on the other hand, is like an inverted pendulum and therefore has a highly unstable system. The most important role in maintaining spine stabilization falls on the muscles around the spine and the muscle group called “core” muscles that wrap the body like a corset. Postural disorders that occur due to the weakening of these muscles over time or the imbalance between the muscles are the source of most spinal problems. The source of common problems such as calcification in the spine, hernias, kyphosis, and low back, and neck pain is often the inability to stabilize the spine. Due to these problems, patients may experience symptoms such as pain with movement, night pains, morning stiffness, decreased range of motion, inflammation, and intra-articular noises during movement.
Although spinal problems are often caused by muscle weakness in old age, there may be reasons such as rapid height increase and muscle imbalance under the problems of patients who have such problems at a young age. For this reason, a good clinical evaluation should be made by considering the characteristics of the patient and the source of the problem should be determined for the correct treatment.
A personalized physical therapy and rehabilitation program should be prepared to ensure the correct alignment and stabilization of the spine and to improve disorders such as hernia and osteoarthritis. Spine rehabilitation includes physical therapy applications such as hot-cold, electrotherapy, some exercises to strengthen and balance the muscles, and manual therapy applications to both reduce the patient’s pain and solve muscle-joint problems.