Pancreas Transplant, Pancreas Transplant Process in Turkey The pancreas is a small organ located in the back of the stomach and in the front of the spine in terms of its location. This organ is responsible for the secretion of hormones called insulin and glucagon. It also balances blood sugar and creates energy stores. In case of damage to this organ, Pancreas Transplantation is applied as a treatment.
- What is Pancreas Transplantation?
- Why is Pancreas Transplantation Performed?
- How is Pancreas Transplant Surgery Performed?
- What are the Risks of Pancreas Transplantation?
- Who is Pancreas Transplantation for?
- Who Cannot Have Pancreas Transplantation?
- Life After a Pancreas Transplant
- Immediate Post-Transplant Recovery
- How to Feed After Pancreas Transplantation?
- Exercising After a Pancreas Transplant
- What Happens During a Pancreas Transplant?
- Who Is a Candidate for the Transplant?
- Pancreas Transplant Prices in Turkey
- Can a Pancreas Transplant be made from a Live Donor?
- What is Required for Pancreas Transplantation?
In this application, a pancreas taken from a cadaver or half a pancreas taken from a living donor is transplanted. In this article that we have researched for you, we will try to find answers to questions such as What is Pancreas Transplantation, Why is Pancreas Transplantation Done, How is Pancreas Transplant Surgery Performed?
What is Pancreas Transplantation?
With the developing and changing technology, there are treatments for diseases that cannot be treated, and now it is easily healed. One of them is Pancreatic Cancer.
The process of removing the pancreas, which can no longer function, and transplanting the pancreas from a cadaver or living donor to a sick person can be written as an answer to the question of What is Pancreas Transplantation? The removed organ is kept in a solution for approximately 20 hours until the operation period.
In the procedures performed, the sick pancreas is not removed from the person’s body. The healthy pancreas is placed in the person’s body to position it on the lower right side of the abdomen, and the veins are connected together as needed. This procedure can be done in four ways: only pancreas transplant, pancreas islet cell transplant, kidney-pancreas transplant, or first kidney and then pancreas transplant.
Why is Pancreas Transplantation Performed?
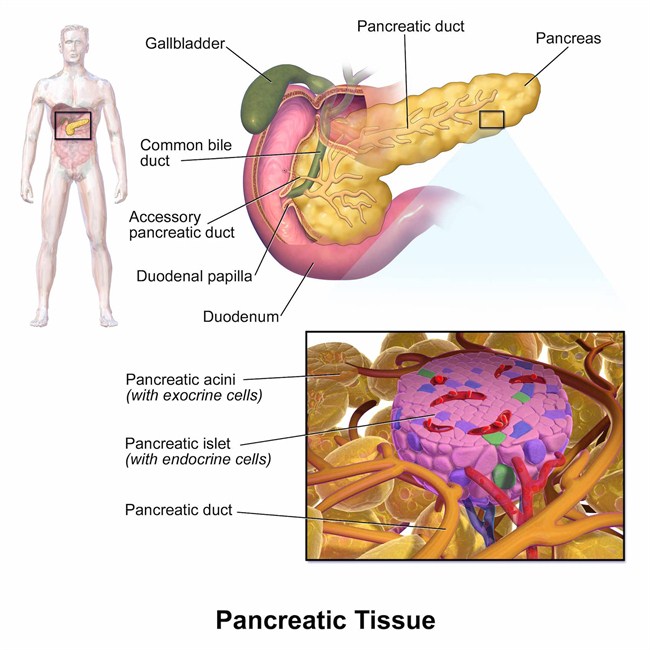
Organ transplants are among the treatments that are easily done today and heal the patient. The life span of the patients is extended by replacing the organs that cannot function due to various reasons with healthy organs. Among these transplants is a pancreas transplant. Why Pancreas Transplantation Is Done, let’s find out together:
- People who have Type 1 diabetes that does not improve as a result of normal treatments that can be done
- People who experience hypoglycemia attacks as a result of frequent drops in blood sugar
- If the body has difficulty in controlling blood sugar
- People who have major kidney problems
- Pancreas transplantation can be performed for people with type 2 diabetes who have low insulin resistance and low production of this insulin
How is Pancreas Transplant Surgery Performed?
People who have serious diseases and need pancreatic surgery urgently have in their minds the question of How to Perform Pancreas Transplant Surgery. The unknown scares people. For this reason, learning about these issues that they are curious about allows the surgery to go smoothly. Let’s learn together how surgery is done.
- When an organ suitable for pancreas transplantation is found, the organ should be transplanted to the body within approximately 18-24 hours. For this reason, the patient whose name is on the organ list and the doctor who will perform the surgery have to wait and wait.
- The operation is performed with the effect of general anesthesia.
- During the operation, the patient’s breathing process is given to the machine. In other words, by intubating, it is provided by respiratory devices.
- During the surgery, the incision starts in the middle of the abdomen and progresses downwards.
- The organ taken from the donor is positioned in the lower part of the patient’s abdomen.
- There is also a small piece of intestine in this organ. This part is also attached to the bladder or bowel.
- The pancreatic veins connected to the leg veins are fed in this way.
- The unhealthy pancreas is left inside the patient. This is because the pancreas aids in digestion.
- Along with a pancreas transplant, the patient may also need a kidney transplant. In this case, the kidneys are also positioned in the lower abdomen and attached to the veins.
- The ureteral organ belonging to the kidneys is attached to the bladder. This organ is in the form of a thin tube that connects the kidney and bladder.
- In the same way, if there is no disease in the kidneys that will cause a problem to remain in the body, these organs are also left in the body.
- During the operation, the patient is monitored by machines. Functions such as blood pressure, pulse, and respiration are kept under constant control. In the event of a contrary situation, immediate intervention is made.
- The operation takes approximately 3-4 hours. If the patient is going to have a kidney transplant, this period may take up to 4-6 hours. Although this period is not clear, it may be longer in case of any complications to be experienced inside.
What are the Risks of Pancreas Transplantation?
Every disease and every treatment method is individual. For this reason, some risks may vary from person to person. One of the most important factors in the realization of risks is the choice of doctor. Doctors who are experts in their field can minimize the risk of risk by coordinating the treatment and surgery process well. Under this title, let’s find out what are the Pancreas Transplant Risks together.
There are risks that may occur during surgery in serious operations such as pancreas transplantation. These are:
- coagulation in the blood
- Intense bleeding
- Infection of the person
- Hyperglycemia or other metabolic problems occurring during surgery
- Risk of urinary tract infection
- Insufficient function of the new pancreas
- Finally, there may be risks such as the body’s rejection of the organ
Who is Pancreas Transplantation for?
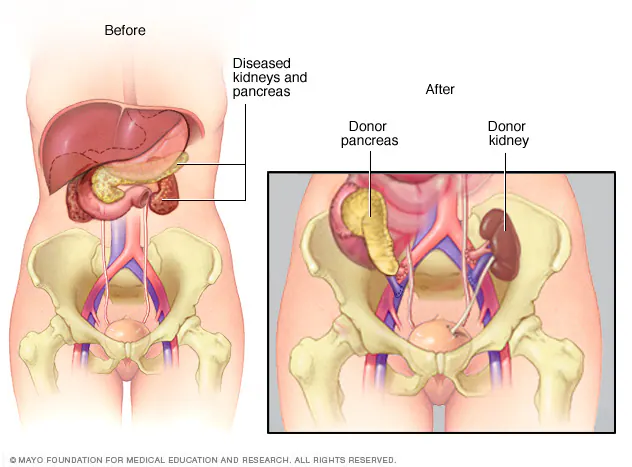
If we answer the question of Who Can Have Pancreas Transplantation; This transplant is done for people who are between the ages of 18-65 and have Type 1 diabetes who are waiting for a kidney transplant. In addition, it is applied to patients who do not have kidney failure, but who have serious and frequent diabetes and insulin disease.
Who Cannot Have Pancreas Transplantation?
After listing the people who will have a pancreas transplant, let’s see who can’t get a pancreas transplant together:
- This transplant is not performed for people with a history of cancer.
- People with HIV/AIDS disease cannot have a pancreas transplant.
- Patients with active hepatitis are not eligible for this transplant.
- Pancreas transplantation is not performed for people who are severely ill with their lungs.
- Pancreas transplantation is not performed for people who are severely obese.
- If the person has vascular occlusion in the neck and legs, pancreas transplantation is not performed for this person.
- If the person; If they are addicted to cigarettes, alcohol or drugs, pancreas transplantation is not performed on these people.
Life After a Pancreas Transplant
A pancreas transplant is a life-changing procedure for individuals with diabetes mellitus, particularly those with severe complications or brittle diabetes. After undergoing this transformative surgery, it’s crucial to understand what comes next. In this article, we will delve into life after a pancreas transplant, discussing the recovery process, potential challenges, and the path to a healthier future.
Immediate Post-Transplant Recovery
After your pancreas transplant surgery, you will spend time in the hospital’s intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring. Here’s a brief overview of what to expect during the initial recovery phase:
Pain and Discomfort: You may experience pain and discomfort at the surgical site, which is normal and managed with pain medications.
Hospital Stay: The length of your hospital stay can vary but generally ranges from one to three weeks. During this time, your medical team will closely monitor your progress.
Regaining Pancreatic Function
Your new pancreas will need time to settle in and begin functioning properly. This process varies from person to person:
Blood Sugar Control: Expect a significant improvement in blood sugar control shortly after the transplant. Many recipients experience freedom from insulin injections and better glycemic stability.
Medications: You will need to take immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted pancreas. These medications will be a lifelong requirement.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Life after a pancreas transplant comes with a few lifestyle changes:
Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet remains crucial. You may need to work with a dietitian to optimize your nutrition and manage your blood sugar levels.
Exercise: Regular physical activity is encouraged to maintain overall health, but it’s essential to discuss any exercise routines with your transplant team.
Immunosuppressive Medications:
Immunosuppressive drugs are vital to prevent your body from rejecting the transplanted pancreas. Adherence to your medication regimen is of utmost importance:
Side Effects: These medications can have side effects, so it’s essential to communicate openly with your healthcare team about any issues you may encounter.
Regular Monitoring: You’ll undergo regular blood tests to ensure your medication levels are adequate and to detect any signs of rejection.
Emotional and Psychological Well-being:
Support System: Lean on your support system of friends and family, and consider joining support groups for transplant recipients to share experiences and advice.
Mental Health: Be mindful of your mental health and seek professional support if needed to cope with the emotional aspects of transplantation.
Follow-Up Care: Your medical team will schedule regular follow-up appointments to monitor your progress, adjust medications, and address any concerns:
Long-Term Care: A pancreas transplant is a lifelong commitment. Regular check-ups and consistent medication management are key to its success.
How to Feed After Pancreas Transplantation?
After the patient has a pancreas transplant and recovers, he or she must be fed a diet in order for the organs to function as they should. For this, he can start this process with expert dietitians. If we talk about How to Feed After Pancreas Transplantation in detail:
- fresh vegetables and fruits
- Foods that contain whole grains
- Fat-free meat, chicken and fish products
- Fibers
- Low-fat milk and low-fat dairy products
- Reducing salt
- Foods that do not contain saturated fats, such as butter should not be on the list
- Apart from this, the person should stay away from alcohol and excessive caffeine consumption
- He should drink plenty of water
- Food should be consumed fresh
- It should be cooked with appropriate cooking methods
- After pancreas transplantation, sleep patterns should be kept under control and exercise should be done to avoid weight gain
Exercising After a Pancreas Transplant
A pancreas transplant is a transformative procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. After this life-changing surgery, adopting a regular exercise routine is crucial to maintain overall health and support the success of the transplant. In this article, we will explore the importance of exercise after a pancreas transplant, the benefits it offers, and how to get started safely.
Understanding the Importance of Exercise After a Pancreas Transplant:
- Enhanced Blood Sugar Control:
- After a successful pancreas transplant, many recipients experience improved blood sugar control. Regular exercise can complement this by increasing insulin sensitivity and helping to maintain stable glucose levels.
- Cardiovascular Health:
- Diabetes can take a toll on the cardiovascular system. Exercise can improve heart health, reduce the risk of heart disease, and enhance overall cardiovascular function.
- Weight Management:
- Some transplant recipients may gain weight post-surgery due to improved nutrition and metabolic changes. Exercise can help manage weight and prevent obesity-related complications.
- Psychological Well-being:
- Exercise has positive effects on mental health, reducing stress and anxiety. After a pancreas transplant, it can contribute to an improved overall sense of well-being.
Getting Started with Exercise After a Pancreas Transplant:
- Consult Your Healthcare Team:
- Before embarking on any exercise program, consult your transplant team. They will assess your individual health status and provide guidance on exercise safety and limitations.
- Start Slowly:
- Begin with low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or stationary cycling. Gradually increase the intensity and duration as your fitness improves.
- Set Realistic Goals:
- Set achievable goals that align with your fitness level and medical condition. Progress may be slower initially, but consistency is key.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Proper hydration is vital, especially for transplant recipients. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
- Monitor Blood Sugar:
- Keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels, particularly if you are taking immunosuppressive medications. Monitor them before, during, and after exercise to ensure they stay within a healthy range.
- Listen to Your Body:
- Pay attention to how your body responds to exercise. If you experience unusual fatigue, dizziness, or any discomfort, stop exercising and consult your healthcare team.
- Incorporate Strength Training:
- Include strength training exercises to build muscle mass and improve overall strength. This can help enhance metabolic health and support weight management.
- Warm-Up and Cool Down:
- Always start with a warm-up and finish with a cool-down to prevent injuries and support muscle recovery.
Conclusion:
Exercise is a vital component of a healthy lifestyle after a pancreas transplant. It offers numerous benefits, including improved blood sugar control, cardiovascular health, weight management, and psychological well-being. However, it’s crucial to exercise safely and consult your healthcare team to ensure it aligns with your unique medical condition.
By incorporating regular exercise into your post-transplant routine and adhering to medical recommendations, you can further enhance the positive outcomes of your pancreas transplant and enjoy a healthier, more active life.
What Happens During a Pancreas Transplant?
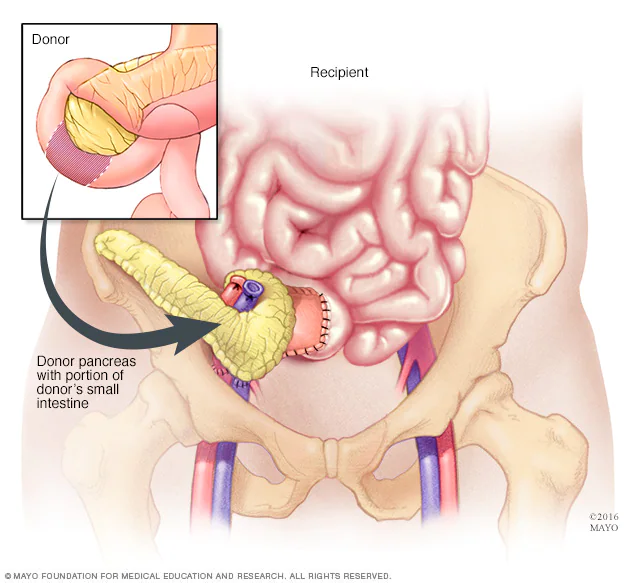
A pancreas transplant is a life-changing procedure that offers hope and improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes mellitus, particularly those with severe complications. But what exactly happens during a pancreas transplant? In this article, we will take you through the process step by step, shedding light on the surgical procedure and what to expect.
- Preoperative Evaluation:
Before a pancreas transplant, candidates undergo a thorough evaluation by a transplant team. This assessment includes:
Medical History: A review of the patient’s medical history, including their diabetes management and any complications.
Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical examination to assess overall health.
Blood Tests: Extensive blood tests to determine eligibility for transplantation and assess compatibility with potential donors.
- Placement on the Transplant Waiting List:
Once deemed eligible, the patient is placed on a pancreas transplant waiting list. The wait time for a suitable donor can vary widely, from months to years.
- Donor Matching:
When a suitable donor pancreas becomes available, a matching process is initiated. Compatibility is determined based on blood type, tissue type, and other factors.
- Surgery Day:
On the day of the transplant, the following steps occur:
Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the lower abdomen, typically on the right side, to access the recipient’s blood vessels and digestive system.
Removal of the Diseased Pancreas: The recipient’s diseased pancreas is carefully removed. In cases of simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplants, the donor kidney is also implanted during this step.
Implantation of the Donor Pancreas: The donor pancreas is connected to the recipient’s blood vessels (artery and vein) and digestive tract. This allows the insulin-producing cells in the new pancreas to function properly.
- Postoperative Care:
Following the surgery, the recipient is closely monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU). This phase involves:
Pain Management: Medications are administered to manage pain and discomfort.
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vital signs and blood sugar levels.
Immunosuppressive Medications: The patient starts taking immunosuppressive medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted pancreas.
- Recovery and Hospital Stay:
The length of the hospital stay varies but typically ranges from one to three weeks. During this time, the medical team monitors the patient’s progress, adjusts medications, and ensures that the transplanted pancreas is functioning correctly.
- Post-Transplant Follow-Up:
After discharge, patients require ongoing follow-up care to:
Monitor the Transplant: Regular check-ups and blood tests are conducted to evaluate the health of the transplant and adjust medications as needed.
Manage Side Effects: Address any side effects or complications, including those related to immunosuppressive medications.
Improve Quality of Life: Support patients in making lifestyle changes to enhance their overall health.
Who Is a Candidate for the Transplant?
Pancreas transplantation is a life-changing procedure that can offer relief and improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes, particularly those with complications that are difficult to manage through other treatments. However, not everyone with diabetes is a candidate for this procedure. In this article, we’ll explore the criteria that determine who qualifies as a candidate for a pancreas transplant and the factors that transplant teams consider during the evaluation process.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes:
Candidates for pancreas transplantation typically have diabetes that is difficult to manage with other treatments. This may include individuals with:
Brittle Diabetes: Unpredictable and severe fluctuations in blood sugar levels despite rigorous management.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness: Inability to detect low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) symptoms, which can be life-threatening.
End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): Individuals who require kidney transplantation due to diabetic nephropathy (kidney damage caused by diabetes) often become candidates for simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplants.
- Age and Health Status:
General Health: Candidates must be in reasonably good health overall to withstand the surgery and the subsequent immunosuppressive medications.
Age: While there’s no strict age limit, candidates should be young enough to enjoy the benefits of the transplant and old enough to minimize the risk of future complications.
- Psychological Evaluation:
Mental Health: Candidates undergo a psychological evaluation to assess their ability to cope with the transplant process and adhere to post-transplant requirements, including medication management.
- Lifestyle Factors:
Tobacco and Substance Use: Smoking and substance abuse can complicate the transplant process and reduce the chances of a successful outcome. Candidates may be required to quit these habits.
Weight Management: Obesity can increase the risk of surgical complications and impact the success of the transplant. Candidates may need to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Social Support:
Support System: Candidates should have a strong support system of family and friends to assist with the recovery process and provide emotional support.
- Commitment to Follow-Up Care:
Adherence: Candidates must demonstrate a commitment to adhere to the post-transplant medication regimen and attend regular follow-up appointments.
- Financial Considerations:
Insurance Coverage: Adequate insurance coverage is essential to cover the costs associated with the transplant and post-transplant care.
- Transplant Center Evaluation:
Transplant Team Decision: Ultimately, the decision regarding candidacy is made by a transplant team, which includes physicians, surgeons, psychologists, and other specialists. They carefully evaluate the candidate’s medical history, overall health, and individual circumstances.
Conclusion:
Pancreas transplantation is a life-altering procedure that can provide relief and improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes who meet specific criteria. The evaluation process is thorough and considers factors such as diabetes control, age, mental health, lifestyle, and social support. It’s essential for potential candidates to work closely with their healthcare team and transplant center to determine their eligibility and explore the best treatment options for their unique circumstances.
Pancreas Transplant Prices in Turkey
A pancreas transplant is a serious procedure that requires serious surgery. For this reason, it is not correct to give precise information about Pancreas Transplantation Prices in Turkey, which foreigners are especially curious about.
Every patient and every illness is individual. For this reason, many factors such as the treatment and treatment methods to be applied, organ transplants that may be needed, the duration of treatment, places to stay, and the hospital to go change the price issue more or less.
For this reason, you can contact us for answers to all the questions you have in mind and for detailed pancreas transplant price information. In addition, if you want to come to Turkey through us and be treated, we can speed up your visa procedures with the invitation letter we sent to the consulate.
Can a Pancreas Transplant be made from a Live Donor?
In the treatment of many diseases, donors from whom organs are taken are people who have brain death, but whose organs are still healthy and alive. For this reason, the question of whether Pancreas Transplantation can be done from a living donor is in the minds of people waiting for an organ.
To answer this question, yes, the donor can be a living person. A part of the pancreas is taken from a living donor and transplanted to the sick person.
What is Required for Pancreas Transplantation?
The answer to the question of what is required for a pancreas transplant can be as follows. After the doctor’s control, it is decided to apply the transplant treatment to the sick person. After this decision, the patient’s name is added to the list of other patients awaiting organ transplantation. When it is his turn and a suitable donor is found, the person is treated by taking surgery.

Vimfay International Health Services