Dermatology is the branch of medicine that deals with diseases of the skin and skin appendages (hair, nails, sweat glands) and mucosa. The skin is the body’s largest organ. The functions of the skin are to filter ultraviolet rays from the sun, maintain body temperature, and maintain water balance. Skin diseases are diseases that often cause cosmetic problems. Methods such as skin biopsy, dermatoscopic imaging, cryotherapy, allergy tests, and phototherapy are used in the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases. In addition, dermatology is examined under two headings as dermatological surgery and cosmetic dermatology. The field of dermatological surgery includes skin biopsies, nail retraction, treatment of skin tumors, and procedures such as removal of moles. The field of cosmetic dermatology covers applications such as botulinum toxin (botox), laser epilation, filling, and hair transplantation.
Acne
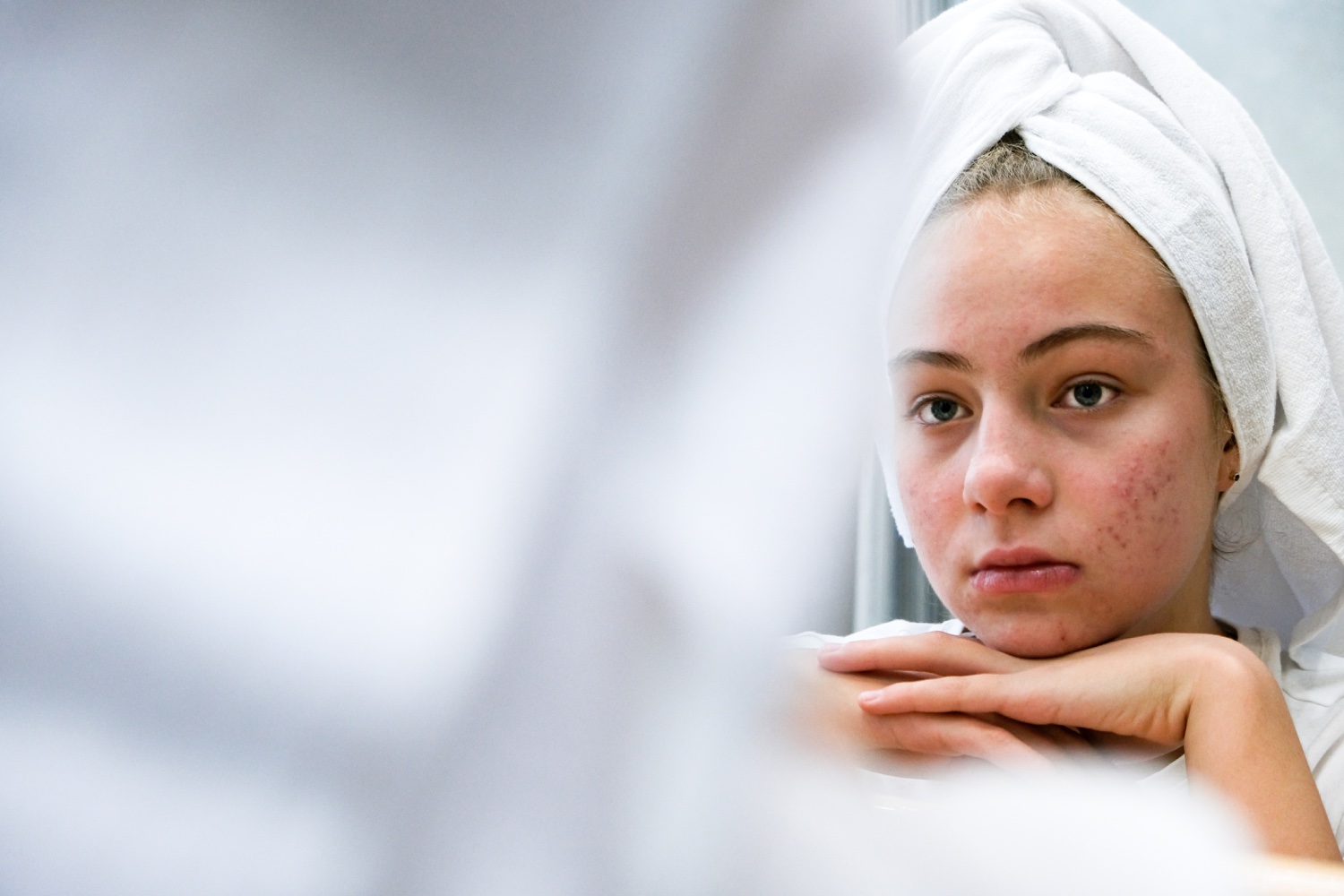

Acne is a skin problem that occurs when the hair follicles on the skin become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Although it is a problem that can affect people of all ages, it is more common in the younger population. Acne symptoms vary depending on the level of the problem. Closed clogged pores (white spots), open clogged pores (black spots), small red tender bumps, swellings with inflammation at the ends, large hard painful nodules under the skin, and painful inflamed cystic lesions under the skin are the most common symptoms of acne.
The four main factors that cause acne problems can be listed as excessive sebum (oil) production, clogged hair follicles due to bacteria, inflammation, oil, and dead skin cells. Acne typically appears on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders. The reason for this distribution is that sebaceous glands (sebaceous glands) are more concentrated in these parts of the body. Hair follicles are also attached to these sebaceous glands. Hair follicles can swell as a result of congestion and form white spots. These white dots can lighten or darken the skin surface, creating blackheads. Blackheads look like dirt accumulated in the pores, but the main reason for this appearance is that the whiteheads are clogged with bacteria and sebum, which turns brown when exposed to air. Nodules (pimples) are red-appearing swellings with a central white periphery that develops when hair follicles become inflamed or infected with bacteria. Blockages and inflammation deep within the hair follicles form cystic lesions just below the skin surface.
High-risk factors for acne problems were determined as hormonal changes, use of certain drugs, a diet rich in carbohydrates, and stress. Contrary to popular opinion, consumption of chocolate and fatty foods, hygiene problems, and the use of cosmetics, as long as they are cleaned regularly, have little effect on acne.
Patients with acne problems usually apply to the clinic when they have acne that does not respond to home care. In addition, sudden onset, and severe acne in advanced age may indicate an underlying disease that requires medical attention.
Acne treatment varies according to the type of acne, its prevalence, and the age of the patient. Medicines such as antibiotics, retinoids, and benzoyl peroxide are used in the medical treatment of acne. Larger cystic lesions can be treated with the drainage method.
Hair and Scalp Diseases
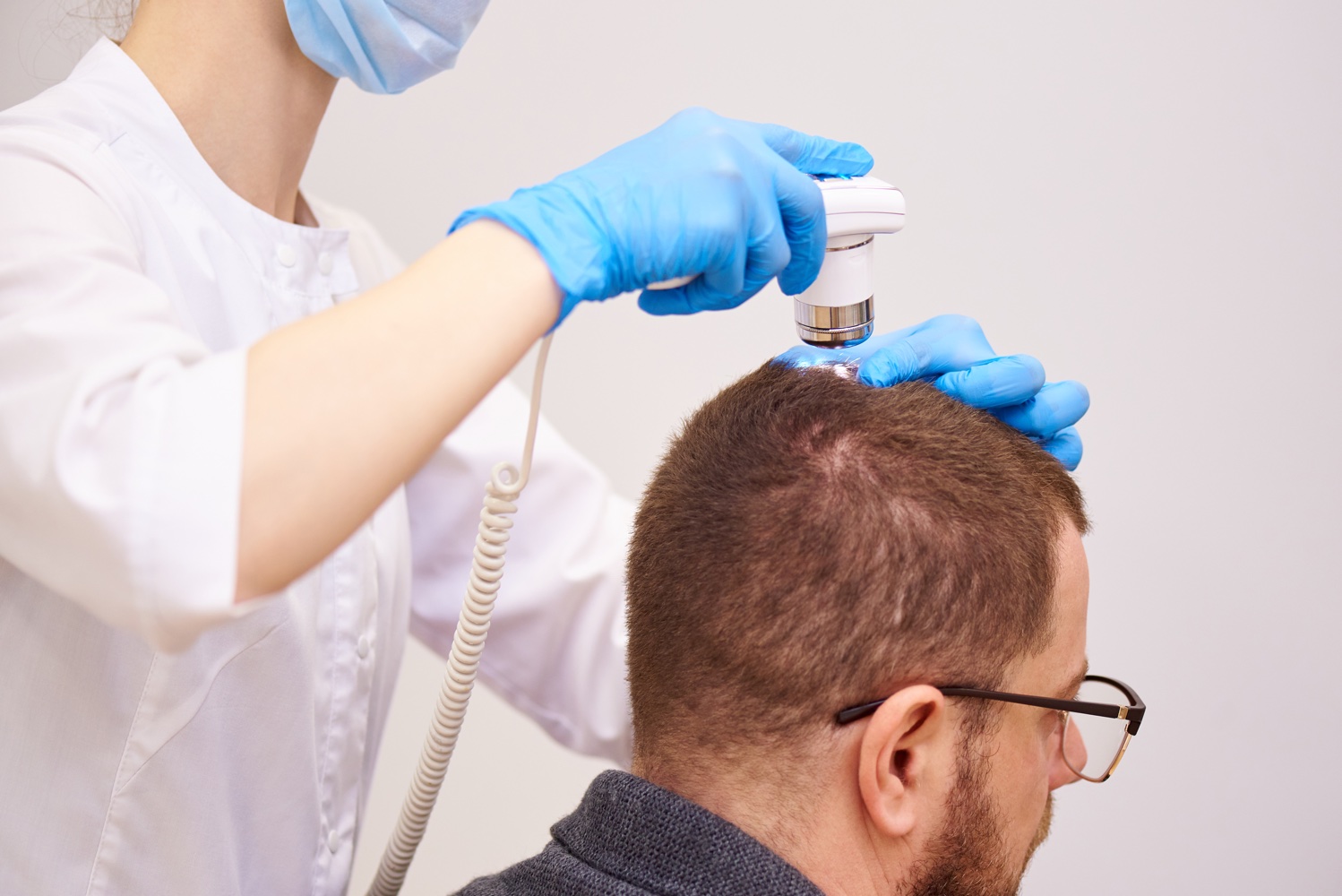
Hair and scalp diseases are mostly seen as cosmetic problems that affect the external appearance of individuals. Common hair diseases are hair loss, dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, cradle cap, head lice,
There are many types of hair loss. Alopecia areata is the condition of hair loss as a result of the immune system attacking the hair follicles. Traction alopecia is the gradual loss of hair exposed to continuous traction due to the use of a ponytail, braid, or protective helmet. Treatment of hair loss varies depending on the type and cause of hair loss. Hair transplant surgeries can be performed on hair diseases that cause permanent hair loss and damage hair follicles.
Dandruff is a problem that occurs with the shedding of a dead scalp. Although the cause is not known exactly, it has been reported that it may be caused by a fungal infection. There is no definite cure for the dandruff problem. However, it is recommended to use shampoos containing coal tar, salicylic acid, selenium sulfide, or ketoconazole.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a more serious scalp problem than dandruff. The scalp looks red and oily. Apart from the scalp, red, oily crusted scaling can be seen between the eyebrows, on the nose skin, and around the ears.
Cradle cap is a type of seborrheic dermatitis seen in babies younger than six months. It can be seen on the baby’s scalp, neck, and around the ears. In its treatment, it is recommended to wash the baby’s head regularly with shampoo suitable for the baby’s skin.
Head lice are small wingless insects that feed on blood. The female ones of the lice that settle on the scalp lay their eggs in the hair. Specially developed shampoos and fine-toothed combs are used in the treatment of head lice. A follow-up of 2 or 3 weeks is recommended to ensure the lice are completely cleared.
Ringworm is a contagious infection that leaves round, scaly, red rashes and balding areas on the scalp. Close contact, and sharing hats, clothes, towels, and combs are ways of transmission. Medications and anti-fungal shampoos are used in its treatment.
Folliculitis is the inflammation of the follicle sacs containing hair follicles. It is usually caused by bacteria that settle in the hair follicles. It is recommended to use antibiotics in its treatment and to keep the area cool, clean, and dry.
Psoriasis is a disease in which itchy, painful, thick-crusted scales are often seen on the scalp due to the body’s continuous production of new skin cells. In its treatment, steroid creams, shampoos containing tar or salicylic acid, and ultraviolet rays are used.
Fungal Diseases
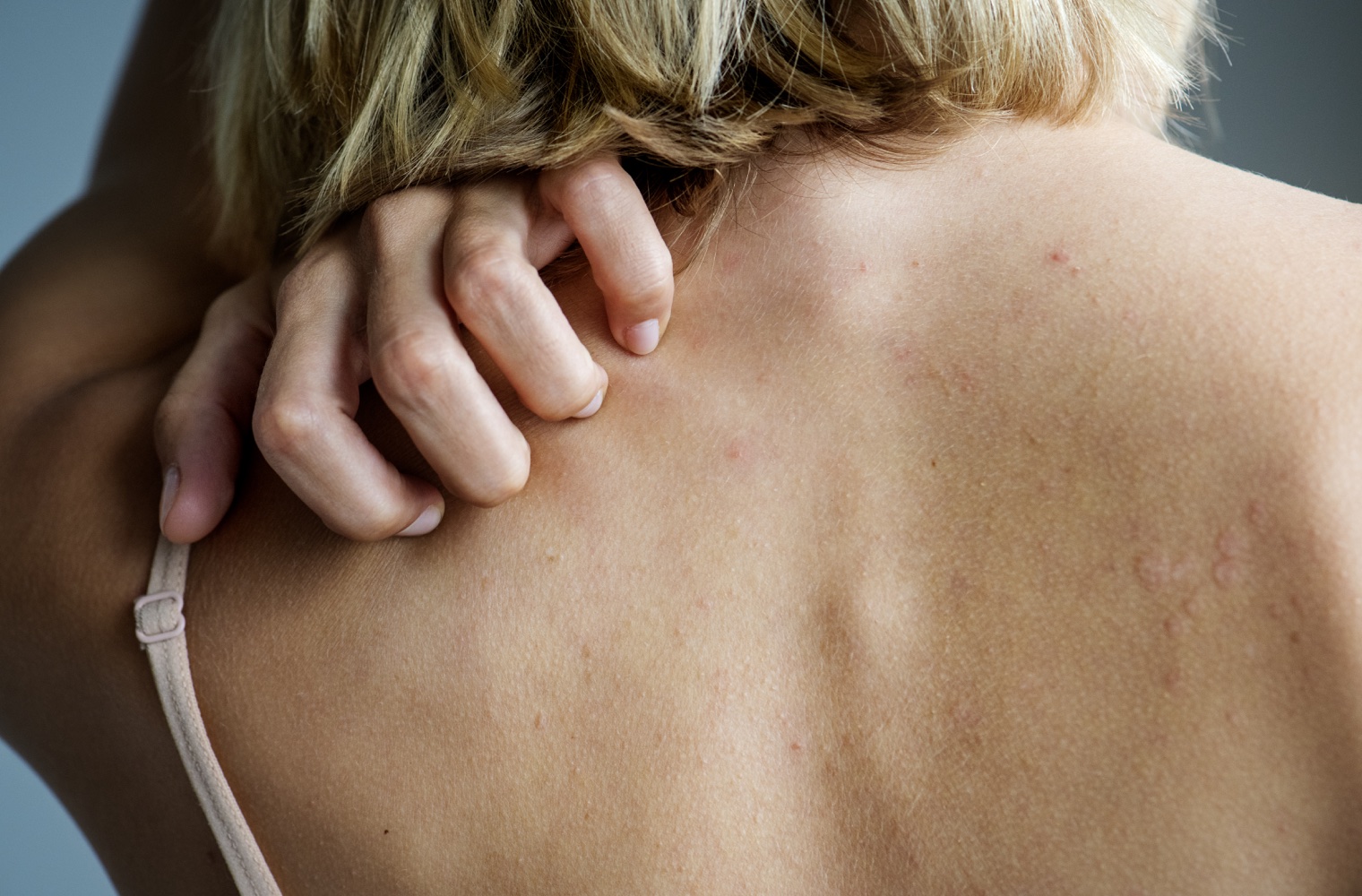
Fungal diseases are one of the most common contagious infectious diseases. Under normal conditions, fungi and bacteria in the body’s natural structure begin to reproduce excessively as a result of the disruption of the balance between them. In case of deterioration of body integrity for any reason, the proliferating fungi enter the body and form a focus of infection. Fungal infections that cause skin redness, rash, itching, and inflammation can be seen in different parts of the body, most commonly the feet, nails, groin area, vagina, and scalp. In the early stages of fungal infections, the limits are clear, but over time, it can spread to other body parts, near or far. Risk factors that increase the incidence of fungal infections can be listed as obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, and diseases affecting the immune system. Fungal species multiply in humid and warm conditions and cause infection. General signs of infection are round-shaped redness, discoloration, scaling, inflammation, and persistent itching of the skin. Fungal diseases are seen in different types according to the area they are in.
Nail fungus (onychomycosis) is frequently seen in the toenails and shows signs such as thickening, discoloration, and deformity of the nail. It can start from one nail and spread to other nails. Foot fungus (tinea pedis) occurs with thickening of the sole and signs of moistening on the side near the little finger. Findings are accompanied by odor and cracks in the future. Vaginal yeast (candidiasis) is a fungal infection of the female external genitalia (vulva) and vagina. atients often apply to the clinic with the complaint of severe itching. Hair fungus (tinea capitis) is a fungal infection that affects the scalp and hair. It progresses with findings such as redness, inflammation, itching, and dandruff. Body fungus (tinea corporis) is a fungal infection that can occur all over the body, except for special areas such as the scalp, nails, hands, and feet.
The diagnosis of fungal infection is made by examining the skin sample taken from the area with laboratory tests. In its treatment, specially produced drugs, creams, and shampoos are generally used. It is important to use medical treatment regularly, as fungi can multiply quite rapidly under suitable conditions. The duration of treatment varies according to the type and localization of the fungus.
It is very important to follow up on the fungal infection in the foot area in patients diagnosed with diabetes. A fungal infection that is overlooked or neglected can cause a wide range of disorders called diabetic foot, ranging from mild sensory impairment to amputation.