Cervical cancer is an important type of cancer that threatens women’s health. While this type of cancer can be successfully controlled with early diagnosis and treatment, it can lead to serious health problems and even death if it is late. Therefore, having information about cervical cancer and knowing its symptoms is of great importance for women to lead a healthy life. In this article we have written for you, we will try to give information about general information about cervical cancer, its symptoms, and its causes.
- What Is Cervical Cancer?
- What Are The Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
- Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
- Screening for Cervical Cancer
- Diagnostic Procedures
- Imaging Tests
- Staging and Treatment Planning
- What Are The Causes of Cervical Cancer?
- Preventing Cervical Cancer
- Vaccination Against HPV
- Regular Pap Smear Screenings
- Practice Safe Sex
- Quit Smoking
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Educate and Raise Awareness
- What Are The Types of Cervical Cancer?
- What Are The Stages Of Cervical Cancer?
- What Are The Risk Factors For Cervical Cancer?
- Is Cervical Cancer Contagious?
- How Is Cervical Cancer Diagnosed?
- What Are The Treatment Methods for Cervical Cancer?
- Cervical Cancer Treatment Prices in Turkey
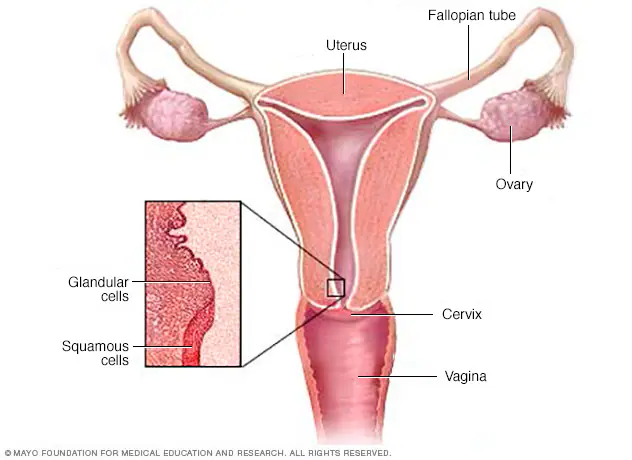
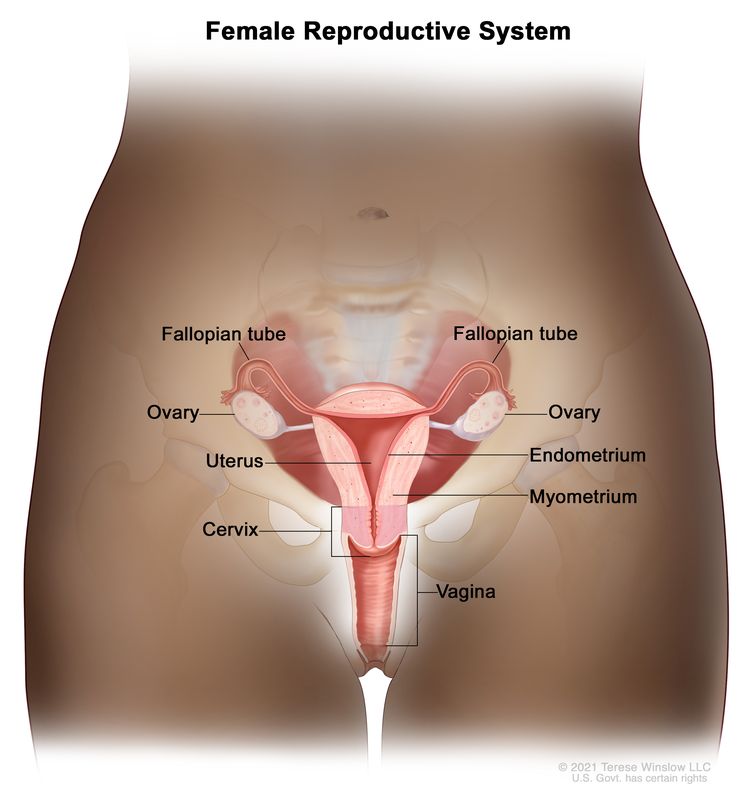
What Is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the area called the cervix, which is located at the bottom of the uterus and opens into the vagina. Although it is usually seen in women between the ages of 30 and 45, it can occur at any age. Cervical cancer can be successfully treated when diagnosed early, especially because it is a type of cancer that progresses slowly. Cervical cancer, one of the most common types of cancer in women worldwide, is especially common in developing countries.
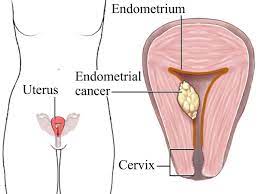
What Are The Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
Symptoms of cervical cancer usually occur as the cancer progresses. It may not give symptoms in the early period and can usually be detected by routine gynecological examinations or smear tests. In the later stages, the following symptoms can be seen;
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding,
- Abnormal vaginal discharge,
- Pelvic pain,
- Pain during sexual intercourse,
- Pain or difficulty urinating,
- Swelling and pain in the legs,
Since these symptoms may also indicate other health problems, it is important to consult a specialist when such complaints are encountered.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a serious health concern that affects many women worldwide. Early detection plays a pivotal role in successful treatment and recovery. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various aspects of diagnosing cervical cancer, from screening methods to confirmatory tests.
Screening for Cervical Cancer
Pap Smear Test: One of the most common screening methods is the Pap smear test. This simple procedure involves collecting cells from the cervix to detect any abnormalities. Regular Pap smears are essential for early identification of potential issues, allowing for timely intervention.
HPV Testing: Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a major risk factor for cervical cancer. HPV testing is often performed alongside a Pap smear to identify the presence of high-risk HPV strains. Early detection of HPV can guide healthcare professionals in providing appropriate care and monitoring.
Diagnostic Procedures
Colposcopy: If abnormalities are detected during a Pap smear or HPV test, a colposcopy may be recommended. During this procedure, a magnifying instrument is used to closely examine the cervix. Biopsy samples may be taken for further analysis.
Cervical Biopsy: A biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the cervix. This sample is then examined under a microscope to determine if cancerous cells are present. Biopsies are crucial for confirming the diagnosis and understanding the extent of the cancer.
Imaging Tests
MRI and CT Scans: Advanced imaging techniques, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans, may be employed to assess the spread of cancer beyond the cervix. These tests provide valuable insights for treatment planning.
Staging and Treatment Planning
After a confirmed diagnosis, the next step involves staging the cancer to determine its severity and extent. Staging guides healthcare professionals in developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
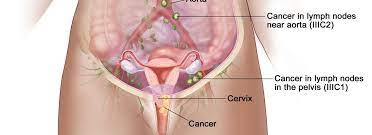
What Are The Causes of Cervical Cancer?
The most important cause of cervical cancer is human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. HPV is a sexually transmitted virus, and some types increase the risk of cervical cancer. However, not all women with HPV infection develop cervical cancer. Other risk factors include;
- Smoking,
- The weakened immune system,
- Multiple sexual partners,
- Starting sexual intercourse at an early age,
- Giving birth in large numbers,
- Long-term use of birth control pills,
Long-term use of birth control pills, To reduce the risk of cervical cancer, it is important to have regular gynecological check-ups and the HPV vaccine. In addition, adopting a healthy lifestyle, not smoking and paying attention to safe sexual intercourse practices also help reduce the risk.
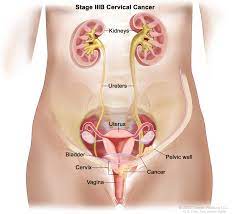
Preventing Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a preventable disease, and by adopting proactive measures, women can significantly reduce their risk. Our comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for preventing cervical cancer and promoting women’s health.
Vaccination Against HPV
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a primary cause of cervical cancer. The most effective way to prevent HPV-related cervical cancer is through vaccination. HPV vaccines are safe, highly effective, and recommended for both young girls and boys. By getting vaccinated early, individuals can build immunity against the most common high-risk HPV strains.
Regular Pap Smear Screenings
Routine Pap smear screenings are vital for early detection of abnormal cervical cells. These screenings can identify precancerous changes, allowing for timely intervention before the development of cervical cancer. Women must follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for the frequency of Pap smear tests.
Practice Safe Sex
Engaging in safe sex practices can reduce the risk of HPV and other sexually transmitted infections. Consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual activity can provide a protective barrier against HPV and other pathogens, contributing to overall reproductive health.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for cervical cancer. Chemicals found in tobacco can damage cervical cells and increase susceptibility to HPV infection. Quitting smoking not only reduces the risk of cervical cancer but also has numerous other health benefits.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and help prevent cervical cancer. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress. A healthy immune system is better equipped to fend off infections, including HPV.
Educate and Raise Awareness
Education is a powerful tool in the fight against cervical cancer. Raising awareness about the importance of prevention, early detection, and vaccination within communities can empower women to take charge of their health. Regular health check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are crucial components of this effort.
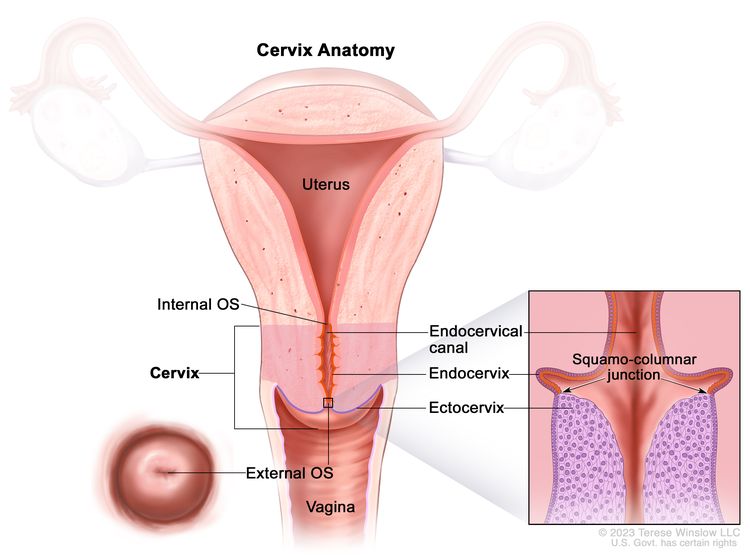
What Are The Types of Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is the formation of malignant tumors that start in the cells of the cervix and grow and spread over time. Cervical cancer is divided into two main types; squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma; Squamous cell carcinoma, which accounts for approximately 80-90% of cervical cancers, originates from thin, flat cells on the outside of the cervix. This type of cancer begins with slowly developing precancerous changes on the surface of the cervix and may develop into cancer over time.
Adenocarcinoma; Adenocarcinoma, which accounts for about 10-20% of cervical cancers, originates from mucus-secreting gland cells in the cervix. This type of cancer develops in the cervical canal and usually follows a more aggressive course.
Other rare types of cervical cancer include adenosquamous carcinoma, small cell carcinoma and carcinosarcoma. Although these types of cancer are less common, they can follow a more aggressive course and regular check-ups are important for early detection.
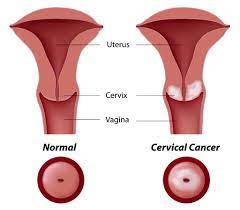
What Are The Stages Of Cervical Cancer?
A staging system is used to determine the degree of spread and treatment options for cervical cancer. The stages of cervical cancer are as follows;
Stage 0; Cancer cells are found only on the surface of the cervix and have not yet spread deeper. At this stage, cancer is considered precancerous and can usually be completely cured by surgery.
Stage 1; Cancer cells have spread into the cervix, but have not yet spread to the uterus and other organs. At this stage, cancer can usually be treated with surgery and radiotherapy.
Stage 2; Cancer has spread to the tissues between the cervix and uterus, but has not yet spread to the pelvic walls and lower abdominal cavity. At this stage, cancer can be treated with surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Stage 3; Cancer has spread to the pelvic walls and lower abdominal cavity. At this stage, cancer can be treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, but the chance of surgical success is low.
Stage 4; Cancer has spread to organs and tissues distant from the uterus and cervix. At this stage, cancer treatment becomes more difficult and treatments to alleviate symptoms with radiotherapy, chemotherapy and palliative care are usually applied.
What Are The Risk Factors For Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer risk factors are factors that increase the likelihood of developing cancer. These factors are as follows;
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection,
- Smoking,
- The weakened immune system,
- Multiple sexual partners,
- Starting sexual intercourse at an early age,
- Long-term use of birth control pills,
- Multiple births,
To reduce the risk of cervical cancer, it is important to have regular Pap tests and HPV vaccination, not to smoke and to be aware of sexual health.
Is Cervical Cancer Contagious?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer characterized by abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cervical cells. This type of cancer is particularly associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. However, cervical cancer is not contagious. This means that contact or being in the same environment as a person with cancer cannot cause cervical cancer in another person.
However, HPV infection is contagious and is a sexually transmitted disease. Some types of HPV can cause cervical cancer, so people infected with HPV have a higher risk of developing cervical cancer. Therefore, it is important to take protection measures during sexual intercourse and have regular screening tests.
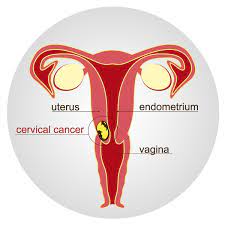
How Is Cervical Cancer Diagnosed?
Cervical cancer can be diagnosed with various tests and evaluations. The first step is usually a gynecological examination. The doctor can examine the vagina and cervix using a speculum to see abnormalities in the cervix. If a suspicious area is found, further tests may be needed;
- Pap smear test,
- HPV test
- Biopsy
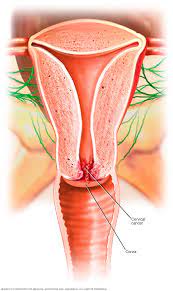
What Are The Treatment Methods for Cervical Cancer?
The treatment of cervical cancer varies depending on the stage of cancer, the general health status of the patient, and personal preferences. The main methods used in the treatment of cervical cancer are as follows;
- Surgical methods can be used to remove cancerous tissue. Conisation is the removal of tissue from the cervix in the form of a cone. Hysteroscopy is the complete or partial removal of the uterus. Removal of lymph nodes can also be done to assess the spread of cancer.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Radiation can be applied externally (external radiation) or with radioactive materials placed inside the body (brachytherapy).
- Chemotherapy uses drugs that stop the growth or kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be used in advanced stages of cervical cancer or to increase the effectiveness of radiation therapy.
- Targeted therapy uses drugs to target specific molecules or proteins that contribute to the growth and spread of cancer cells. This treatment may be an option for patients with cervical cancer that is resistant to chemotherapy.
Cervical cancer treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach and supportive care is important to maintain the patient’s quality of life. Lifestyle changes such as psychological support, nutrition and exercise also play an important role in the treatment process.
Cervical Cancer Treatment Prices in Turkey
Turkey has managed to announce its name to the world with its investments and studies in the field of health. Especially the latest technological devices used in diagnosis and treatment procedures have been a beacon of hope for many diseases. However, there has been an increase in health tourism in Türkiye.
- Hospitals are large, clean, spacious and fully equipped in terms of technological equipment.
- Turkish doctors are specialized, successful, and skilled in their fields.
- Nurses and carers are friendly and compassionate.
- Finding answers to the questions asked quickly and accurately.
- Patience and understanding of all staff, including the intermediary company dealing with the patient.
- Turkey offers holiday opportunities with its natural and historical beauties.
- Easy transportation.
- Diagnosis, treatment, accommodation, eating, drinking, dressing, and holiday needs can be met at affordable prices.
Such situations are shown among the reasons for preference. We can see that patients and relatives of patients who want to come to Turkey are doing research on Cervical Cancer Treatment Prices in Turkey. However, it would not be correct to give clear price information at this stage. Many factors such as the type of disease, stage, diagnosis process, treatment process, and stay in Türkiye affect the price issue. If you want to get more detailed price information, you can contact us. In addition, if you come to Turkey for treatment through us, we can facilitate your visa application process with the invitation letter sent by us to the consulate.

Vimfay International Health Services